Employee autonomy at work: The catalyst to effective employee engagement

Have you ever wondered how much control your employees have over the work they do? Does it make them confident and empowered to share their ideas or do they fear being humiliated and negated? Do you feel your employee engagement rate is satisfactory?
Answering these questions is of utmost importance for your employees!

University of Michigan's Gretchen Spreitzer studied 20 years of workplace empowerment research and found eye-opening benefits of autonomy for employees. Higher job satisfaction, productivity, performance, employee motivation, and lower turnover/burnout were a few elements on top of the charts.
It’s high time organizations open the door of freedom for their employees and change the dynamics of their organization. It is essential for you, as a leader, to channelize your energy towards doing great work instead of controlling and micromanaging your employees, thus building an atmosphere of autonomy at the workplace.
The evolution of businesses necessitates leaders to give employees the room to perform their best. To pursue unique ideas and make smart decisions, employees require flexibility and autonomy at work.
But here’s the issue: Leaders often find it difficult to draw a line and resolve the tension between employee freedom, operational excellence, and discipline.
It’s important for managers to understand the need for autonomy and trust that devising a broad strategy with collaboration is not the end of freedom. Crafting a framework, motivating employees to thrive, and achieving organizational success can help employees work autonomously and spark a commitment to contribute to the overall growth of organizations.
Managers must not question themselves whether they should give autonomy rather ask what kind of autonomy should be given. This creates a high level of trust amongst employees which increases levels of ownership leading to business success.
What does autonomy mean?

As per Harvard Business Review, “Autonomy is a feeling of being in control and having a choice. When we have choices, we experience natural rewards of feeling positive.”
“52% of employees feel the absence of autonomy in their work.”
Some of the most important characteristics that build autonomous workplaces are:
- Capacity to make decisions: Autonomous employees have the competence and are given the flexibility to make decisions for themselves. Employees do not have to run every decision through their leaders or take approvals for every petty work.
- Support creative ideas: When employees feel like their ideas and contributions are being valued, their contribution and effort levels increase. For example; Google designed the “20 percent time” concept where they allowed employees to spark creativity and ideate on G-related passion projects which gave birth to some fascinating strategies like Gmail, Google Maps, etc.
- Incorporate flexibility: Employee autonomy gives them the flexibility to determine their own responsibilities and manage their work schedules keeping the end goal in mind. Flexibility and autonomy go hand in hand and these characters are becoming a gender-neutral issue.
- Encourage open communication: Autonomy is closely tied to effective communication. In autonomous workplaces, open and transparent communication channels are essential. Employees should feel comfortable expressing their ideas, concerns, and feedback without fear of repercussions.
- Provide opportunities for skill development: Autonomous workplaces prioritize employee growth and skill development. They offer resources, training, and mentorship programs that empower employees to expand their skill sets and take on new challenges.
- Recognize and reward autonomy: Acknowledging and rewarding employees for their autonomous efforts fosters a culture of empowerment. Recognizing those who excel in making independent decisions and driving positive outcomes reinforces the value of autonomy within the organization.
- Embrace a culture of trust: Autonomous workplaces are built on trust. Employees are trusted to carry out their responsibilities with integrity and professionalism. Trusting employees not only boosts morale but also enhances their sense of ownership and responsibility.
- Promote work-life balance: Autonomy extends to managing one's work-life balance. Autonomous workplaces recognize the importance of employees' personal lives and encourage practices that ensure a healthy equilibrium between work and personal commitments.
- Encourage continuous learning: Autonomous workplaces value a growth mindset and encourage employees to pursue continuous learning. They provide access to learning resources, encourage participation in workshops and seminars, and support employees in staying updated with industry trends and best practices.
- Foster a culture of innovation: Autonomous workplaces thrive on innovation. Encouraging employees to think outside the box and take calculated risks fosters a culture of innovation where new ideas can flourish. This atmosphere of innovation not only benefits the organization but also keeps employees engaged and motivated.
- Promote collaborative decision-making: While autonomy grants individuals the freedom to make decisions, it's also important to foster collaboration in decision-making processes. Encouraging teams to work together and leverage collective intelligence can lead to better decision outcomes and a stronger sense of ownership among team members.
Why give employees autonomy?

Have you ever wondered why some companies grant their employees more autonomy? It's not just about being generous or trendy; there are solid reasons behind it. Let's dive into why giving employees autonomy is a winning strategy.
First and foremost, autonomy breeds trust. When you empower your team members to make their own decisions, you're essentially saying, "I trust you." This trust creates a positive work environment where employees feel valued and respected.
Furthermore, autonomy fuels motivation. When people have ownership over their own schedule, tasks and projects, they're more likely to be passionate and driven. This intrinsic motivation can lead to higher job satisfaction and productivity.
Autonomy also nurtures creativity. When employees are free to explore different approaches and solutions, innovation flourishes. New ideas emerge, and your company can stay ahead in a constantly evolving market.
Moreover, it boosts employee retention too. Employees who have autonomy are less likely to feel stifled or micromanaged, which can be a major factor in job satisfaction. They're more likely to stay with your company, saving you time and resources on recruitment and training.
15 Benefits of autonomy in the workplace

Many employees crave autonomy in the workplace, and for good reason. Autonomy, or the freedom to make choices and take ownership of your work, can be a game-changer for both employees and employers. In this article, we're going to explore 15 compelling benefits of autonomy in the workplace that will make you want to embrace it wholeheartedly.
- Enhanced job satisfaction: Autonomy empowers employees to take charge of their tasks, leading to a greater sense of achievement and job satisfaction.
- Increased productivity: When individuals have control over their work, they tend to be more engaged, focused, and productive.
- Boosted creativity: Autonomy encourages employees to think outside the box, fostering a culture of innovation within the organization.
- Better time management: With autonomy, employees can prioritize tasks and manage their time efficiently, reducing stress and burnout.
- Personal growth: Autonomy offers opportunities for skill development and personal growth as employees tackle challenges independently.
- Greater accountability: When individuals have autonomy, they take responsibility for their decisions and actions, resulting in higher accountability.
- Improved decision-making skills: Autonomy hones decision-making abilities, as employees learn to weigh options and make informed choices.
- Stronger employee engagement: Autonomy gives employees a sense of ownership in their work, leading to increased engagement and commitment.
- Enhanced problem-solving: Autonomous workers are more adept at problem-solving, as they tackle challenges head-on without relying on constant guidance.
- Reduced micromanagement: Autonomy reduces the need for micromanagement, freeing up managers to focus on strategic tasks.
- Flexibility: Employees with autonomy often have more flexibility in their work schedules, promoting work-life balance.
- Higher retention rates: Companies that offer autonomy tend to retain top talent longer, as employees feel valued and empowered.
- Competitive advantage: Organizations that embrace workplace autonomy are often more agile and adaptable, giving them a competitive edge in today's dynamic business landscape.
- Encourages innovation: Employees feel empowered to experiment with new approaches and solutions, leading to groundbreaking innovations that drive the organization forward.
- Promotes diversity and inclusion: Autonomy promotes diversity of thought and inclusion in the workplace. When employees have the freedom to express their unique perspectives and ideas, it leads to a richer and more inclusive work culture.
What are the common causes of a lack of autonomy in the workplace?

Many workplaces struggle to provide employees with the autonomy they need to thrive. Understanding the common causes of a lack of autonomy in the workplace is crucial for organizations seeking to foster a culture of empowerment and innovation.
By identifying and addressing these underlying causes, organizations can create an environment where employees feel empowered to take initiative, make decisions independently, and drive success.
- Micromanagement: One of the primary causes of a lack of autonomy in the workplace is micromanagement by supervisors or managers. When leaders excessively monitor and control every aspect of employees' work, it can leave little room for individuals to make decisions independently.
- Hierarchical structures: Organizations with rigid hierarchical structures may inadvertently stifle autonomy. In such environments, decision-making authority is often concentrated at the top levels of management, leaving lower-level employees with limited autonomy to make significant decisions.
- Lack of trust: A fundamental lack of trust between management and employees can also contribute to a lack of autonomy. When leaders do not trust their team members to handle responsibilities autonomously, they may resort to imposing strict controls and oversight, further undermining autonomy in the workplace.
- Unclear expectations: When employees are unsure about what is expected of them or how their performance will be evaluated, it can hinder their ability to exercise autonomy. Without clear guidelines and expectations, individuals may hesitate to take initiative or make decisions independently.
- Fear of failure: In environments where failure is not tolerated or punished, employees may be reluctant to take risks or make decisions autonomously. The fear of making mistakes can lead individuals to seek constant approval or avoid taking on challenging tasks altogether, limiting their autonomy in the process.
- Lack of training and development: A lack of opportunities for skill development and training can also contribute to a lack of autonomy in the workplace. When employees do not have the necessary knowledge or resources to handle tasks independently, they may rely more heavily on supervision and guidance from others.
- Organizational culture: The prevailing culture within an organization can significantly impact autonomy in the workplace. Cultures that prioritize control, conformity, and adherence to strict procedures may inhibit autonomy, whereas cultures that value innovation, empowerment, and trust are more likely to foster autonomy among employees.
- Overemphasis on compliance: In industries or organizations where compliance and adherence to regulations are paramount, there may be a tendency to prioritize conformity over autonomy. Strict adherence to rules and regulations can limit employees' ability to exercise autonomy in decision-making processes.
The relationship between autonomy and flexibility

Autonomy is like the trusty captain of a ship. It empowers employees to steer their own course, make decisions, and take ownership of their work. Flexibility, on the other hand, is the adaptable first mate, allowing employees to navigate changing tides with ease. Together, they create a powerful synergy.
When employees have autonomy, they can often choose when, where, and how they work best. This flexibility leads to improved work-life balance, reduced stress, and increased job satisfaction. It also means that employees can adjust their schedules to accommodate personal needs or unexpected life events without sacrificing productivity.
Conversely, flexibility enhances autonomy. It allows employees to tailor their work environment to suit their preferences, whether that's working from home, a coffee shop, or a traditional office. This sense of control over their surroundings further boosts their autonomy and overall job satisfaction.
What is lack of autonomy in employees?

A lack of autonomy in employees refers to a situation where individuals have limited independence and decision-making power in their roles. They may have to follow strict guidelines, adhere to rigid processes, and receive constant oversight from superiors.
The impact on employees:
- Decreased job satisfaction: When employees don't have a say in how they perform their tasks, it can lead to decreased job satisfaction. They may feel like mere cogs in a machine, which can be demotivating.
- Reduced engagement: Autonomy often fuels employee engagement, but without it, employees may become disengaged. They might go through the motions without feeling a sense of ownership or passion for their work.
- Increased stress: A lack of autonomy can lead to increased stress levels. Employees may feel pressured to meet strict guidelines and may experience anxiety about making mistakes.
- Limited creativity: Autonomy encourages creative thinking and problem-solving. Without it, employees may struggle to think outside the box or come up with innovative solutions.
- Higher turnover: Employees who feel stifled and powerless are more likely to seek opportunities elsewhere. High turnover can be costly for organizations and disrupt team dynamics.
- Impaired decision-making skills: When employees are denied opportunities to make decisions, their decision-making skills can deteriorate. This can hinder their ability to handle complex tasks or projects independently.
- Lower productivity: A lack of autonomy can lead to lower productivity as employees may lack the motivation and sense of ownership needed to excel in their roles.
How lack of autonomy in the workplace affect business?

Reduced employee morale and engagement
When employees feel like their voices and ideas don't matter, their morale and engagement plummet. They may become disinterested, leading to lower productivity and creativity.
Stifled innovation
Innovation thrives in an environment where employees are encouraged to experiment and think creatively. A lack of autonomy can stifle these innovative sparks, hindering your company's ability to adapt and evolve.
Diminished problem-solving
Autonomy fosters critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Without it, employees may struggle to tackle challenges independently, affecting the company's ability to overcome obstacles efficiently.
Declining productivity
Autonomy often translates into increased responsibility and accountability. Without it, employees may feel less motivated to excel, leading to decreased productivity.
Poor decision-making
When employees aren't empowered to make decisions, the burden falls on higher-level management, potentially overwhelming them. Decisions may be delayed or poorly made due to a lack of diverse perspectives.
Negative workplace culture
A culture of control and micro-management can breed resentment and erode trust. This can harm relationships among employees and between employees and management.
How to enable employee autonomy in hybrid workplaces?
Control! Even the thought of it sounds comforting, especially if you are the boss. But, leaders are accepting the necessary change required.
Before you bring autonomy to your workplace, understand that there is no one-size-fits-all framework for enabling employee autonomy. Different employees have different needs and working styles. While some work better under supervision, others outperform when given the freedom. It is essential for leaders to understand and familiarize themselves with employees through regular conversations.
“Autonomy at work increased employee productivity by 5.2% on an average”
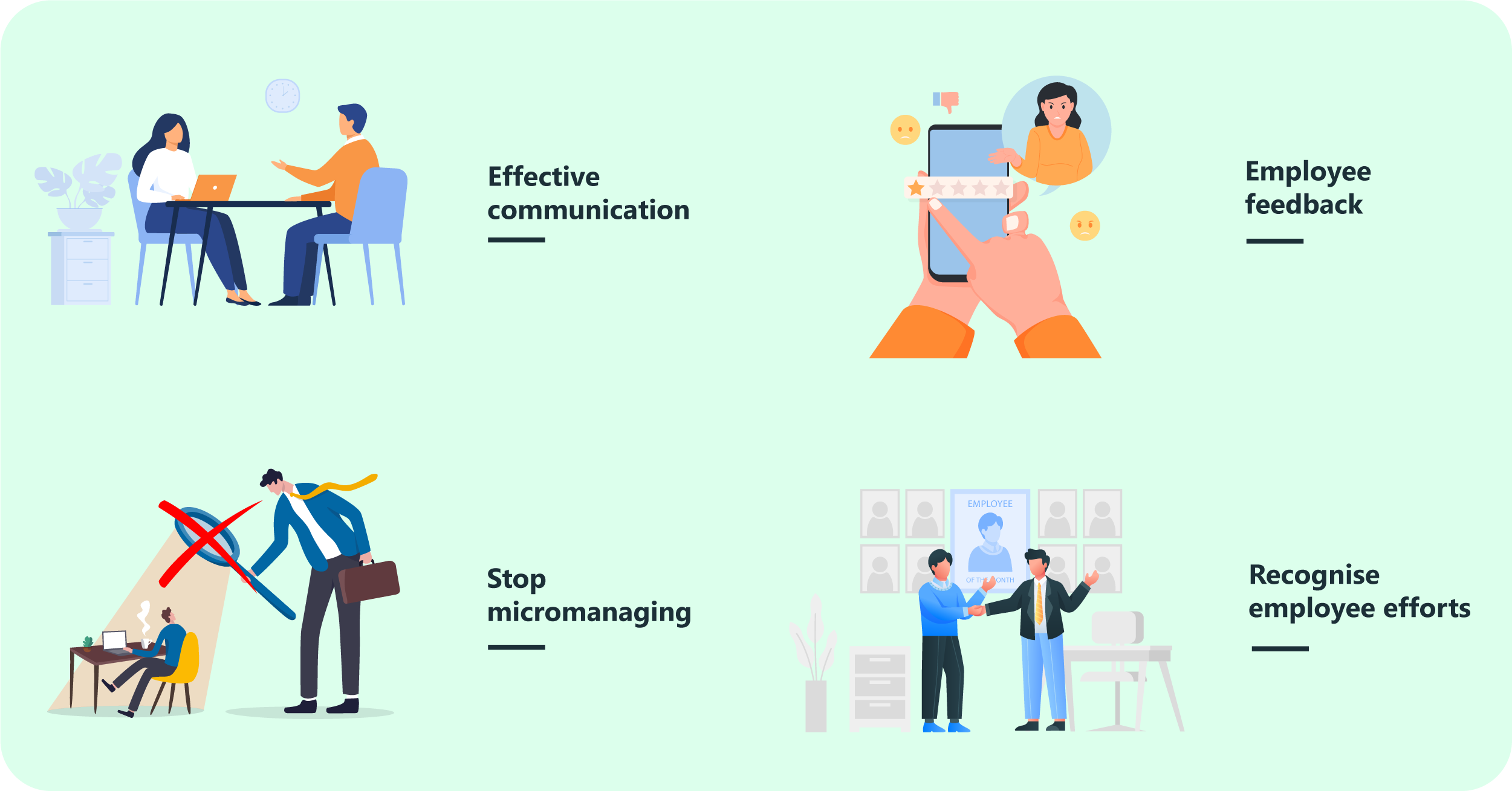
Why is autonomy important more than ever in these uncertain times? With workplaces adopting the hybrid model, leaders face hurdles while enabling employee autonomy. If you happen to be in the same position, follow these steps for a smooth transition.
Step 1: Effective communication:
Management cannot expect employees to execute strategies without communicating the strategic intent. That is why leaders must communicate their vision and design a framework collectively and then leave employees in automation mode. Communicate what you expect and encourage and establish a two-way communication channel with a clear sense of autonomy.
Step 2: Seek employee feedback:
Every employee has their own process and a different expectation of autonomy from their leaders. Seeking proper feedback on what works for the employees and how they want to add autonomy for future projects will increase employee engagement, productivity, and delivery.
Step 3: Stop micromanaging:
Eliminating spoon-feeding on the front foot but conducting meetings frequently to gain insights on employee progress and giving unconstructive feedback curbs employee autonomy. Rather create a blueprint for projects and engage weekly for creative brainstorming and empowering employees to communicate with each other as and when they are stuck.
According to Gartner, 9% of the surveyed employees felt more productive with less management supervision”
Step 4: Recognise employee efforts:
Encourage employees to fall while creating guardrails for them. Recognizing and rewarding autonomous employees boosts confidence in them. Celebrating small wins creates a sense of belongingness. It could be as small as a “Thank You” note or as big as a bonus.
Step 5: Foster a culture of trust:
In a hybrid workplace, trust becomes paramount. Encourage leaders to trust their employees' judgment and decision-making abilities. When employees feel trusted, they are more likely to take ownership of their work.
Step 6: Provide autonomy within boundaries:
Set clear boundaries and guidelines for employee autonomy. While giving them the freedom to make decisions, ensure that they understand the limits and consequences of their choices. This balance between autonomy and boundaries creates a sense of responsibility.
Step 7: Offer autonomy training:
Invest in training programs that help employees develop the skills needed to thrive in an autonomous work environment. These programs can include decision-making, time management, and effective communication skills.
Step 8: Embrace technology:
Utilize technology to enable and support employee work autonomy even in hybrid workplaces. Implement collaboration tools, project management software, and communication platforms that facilitate remote work and empower employees to work autonomously.
Step 9: Encourage peer support and collaboration:
Create opportunities for employees to support each other and collaborate on projects. Foster a culture encouraging autonomy where colleagues can share knowledge, offer assistance, and collaborate on tasks, even in a hybrid work setting.
How to encourage autonomy at work: 8 Ways

Autonomy in the workplace can be a game-changer, and as a leader or manager, you have the power to encourage it. Let's explore nine effective ways to foster autonomy in your team.
- Set clear expectations: Start by defining clear goals and expectations for each project or task. When employees know what's expected of them, they can confidently take ownership of their work.
- Provide training and resources: Empower your team with the knowledge and tools they need to excel independently. Offer training sessions, access to resources, and opportunities for skill development.
- Offer support, not micro-management: Resist the urge to micromanage. Instead, provide support and guidance when needed, allowing your team members to take the lead and learn from their experiences.
- Encourage initiative: Reward and acknowledge initiative. When employees take the initiative to propose new ideas or solutions, celebrate their efforts, even if the outcome isn't always perfect.
- Delegate authority: Delegate decision-making authority whenever possible. Let team members make choices about how to approach tasks and projects within the boundaries you've set.
- Embrace mistakes: Create a culture that doesn't penalize mistakes but views them as opportunities for growth. When employees know they won't be reprimanded for trying something new, they're more likely to take calculated risks.
- Recognize achievements: Celebrate and recognize achievements, both big and small. Publicly acknowledge the successes of your team members to boost morale and motivation.
- Regular feedback: Foster open communication with regular feedback sessions. Allow employees to share their thoughts, concerns, and ideas. This two-way dialogue promotes a sense of ownership and accountability.
How to empower managers within the employee engagement ecosystem?
As per research, 79% of employees are engaged when given autonomy at work and thus show increased accountability and performance output.
Leaders are inclined towards empowering autonomous teams. They have started to believe that this is the obvious step to foster innovation, creativity, and growth. But, they are also afraid of the chaos followed by freedom.

It’s possible to create a proper structure and control — while also giving your employees the autonomy they expect. How? By empowering managers to design guardrails that will help leaders make a real change.
Managers need to constantly make efforts to listen to their employees through pulse surveys and subsequently take actions based on real-time insights. In most organizations, managers fail to take follow-up actions due to their workloads or because they disregard the importance of timely actions after surveying the employees.
To solve these problems, CultureMonkey designed manager dashboards that can help team leaders assess the problem areas and draft a strategy to solve them by looking at comprehensive reports. On failing to take action, the system sends timely nudges and alerts to help them prioritize the mechanism.
Thus, truly enabling them to make action items a priority of value as opposed to a “task” that they need to complete. Here are some of the measures that you can take as a manager to bring in autonomy in workplaces.
1. Nurture a strategic mindset:
Instill an autonomous strategic mindset for employees, a mindset where everyone from top to bottom has a fair understanding of the business operations, strategic plans, and know-how about the impact of their projects on the larger goal of the organization.
Equipping people with such information will eliminate misinterpretations and communication gaps increasing efficiency as they’ll understand the purpose and value of their work.
2. Distribute risk mitigation:
Customer-focused companies have a lot of quality standards to deliver identical experiences to each customer. It’s natural for such companies to fear autonomy as it could put their reputation at stake. But, a lack of autonomy will make things worse for companies.
To mitigate risk, design a framework and educate employees on customer delivery. Hand on the responsibility in each hand for not exposing the company to risk that could hurt it.
3. Build a culture of trust:
A study from ManpowerGroup Solutions suggested that nearly 40% of employees worldwide said that autonomy is one of their top three factors in career decisions.
4. Foster collaboration:
Create opportunities for cross-functional collaboration. When employees from different departments work together on projects, it promotes autonomy by allowing them to leverage each other's expertise and make collective decisions
5. Provide autonomy training:
Invest in training programs that specifically focus on autonomy and decision-making. Equip managers with the tools and knowledge to support their teams in becoming more autonomous. Training can help bridge the gap between understanding the concept of autonomy and implementing it effectively.
6. Establish clear metrics:
Define clear metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) that align with the organization's goals. This provides employees with a sense of purpose and direction, allowing them to make autonomous decisions that contribute to achieving these objectives.
A culture of trust provides employees with the cushion to share their ideas, problems, or roadblocks. Not trusting your employees can lead to micromanaging impacting their behavior, morale, and engagement.
Rather, having a culture of trust and autonomy at workplaces will empower managers to consult employees about their tasks, encourage new ideas and allow two-way feedback.
50+ Autonomy at work questionnaire

Autonomy, or the freedom to make decisions and take ownership of your tasks, is a vital aspect of job satisfaction and productivity. To help you gauge your level of autonomy at work, we've put together a comprehensive questionnaire with 50+ thought-provoking questions.
- Do you have the flexibility to choose when and where you work, to some extent?
- Are you allowed to make decisions about how you complete your tasks?
- Can you propose new ideas or projects without seeking constant approval?
- Do you have the authority to allocate resources for your projects?
- Are you encouraged to set your own goals and priorities?
- Can you modify your work processes or methods to increase efficiency?
- Are you trusted to handle unexpected challenges without immediate supervision?
- Can you select your preferred tools and software to complete tasks?
- Are you involved in determining your own performance metrics and goals?
- Do you have the autonomy to delegate tasks to team members when appropriate?
- Are you allowed to choose your own professional development opportunities?
- Can you adapt your work schedule to accommodate personal needs?
- Are you encouraged to take calculated risks in your role?
- Do you have the autonomy to negotiate agreements and contracts with clients or partners?
- Can you suggest changes to policies or procedures that affect your work?
- Are you trusted to manage your own workload without excessive oversight?
- Can you decide how to prioritize and organize your tasks?
- Are you allowed to experiment with new technologies or approaches in your work?
- Can you take on leadership roles in projects when you feel capable?
- Do you have input in the selection of team members for collaborative projects?
- Are you encouraged to seek out and implement innovative solutions to problems?
- Can you set your own deadlines for tasks and projects within reason?
- Do you have the autonomy to work on projects that align with your interests and strengths?
- Can you suggest changes to your job description or role based on evolving responsibilities?
- Are you trusted to manage your own budget or financial resources for projects?
- Can you work on personal growth and skill development during office hours?
- Are you involved in decisions regarding your compensation and benefits?
- Can you choose your own training and development programs?
- Do you have the authority to make hiring or firing decisions in your department or team?
- Are you encouraged to take ownership of the outcomes of your projects?
- Can you represent your organization in negotiations, meetings, or conferences independently?
- Do you have the autonomy to decide whether to collaborate with external partners or vendors?
- Are you trusted to communicate directly with clients or customers without constant supervision?
- Can you propose changes to the organizational structure or hierarchy?
- Are you allowed to determine your own working hours within reason?
- Can you decide how to allocate your time between different tasks and projects?
- Do you have the freedom to work on projects that align with your values and principles?
- Are you encouraged to express dissenting opinions or challenge conventional wisdom in decision-making processes?
- Can you participate in cross-functional teams or projects outside of your immediate scope of work?
- Are you empowered to take breaks or time off when needed without feeling guilty or judged?
- Do you have the autonomy to pursue side projects or passion projects related to your work?
- Can you choose the communication channels and methods that best suit your needs and preferences?
- Are you involved in strategic planning and long-term vision-setting for your team or department?
- Do you have the authority to represent your team or department in discussions with upper management?
- Are you encouraged to share knowledge and expertise with colleagues through mentorship or training programs?
- Can you initiate and lead process improvement initiatives within your team or department?
- Do you have the autonomy to choose the vendors or suppliers for projects or initiatives?
- Are you trusted to manage confidential or sensitive information responsibly and ethically?
- Can you decide how to allocate resources between competing projects or priorities?
- Do you have the freedom to work remotely or from different locations as needed?
- Are you encouraged to challenge the status quo and suggest alternative approaches or solutions?
- Can you take ownership of mistakes or failures without fear of punitive action?
- Do you have the autonomy to negotiate work arrangements or accommodations that meet your needs?
- Are you empowered to escalate issues or concerns to higher management when necessary?
Conclusion
In the words of Frank Tyger: “Doing what you like is freedom. Liking what you do is happiness."
Netflix, a US-based media company stated its culture as a blend of “freedom and responsibility”. They believe employees perform best when they do not have to ask for approvals for every petty thing. The company gives employees full autonomy to choose their vacation time, maternity leave, etc by minimizing rules and valuing flexibility over efficiency.
One of the executives mentioned, “We want to help people learn and give them oxygen to make mistakes.” All these approaches paid off for Netflix. From being a mail-order video-rental service, Netflix expanded into online streaming with more than 100 million subscribers worldwide. The company gives the credit of its success to its empowered, committed, and engaged workforce.
If you envision scaling up your organization exponentially, then drive your purpose into actions eminently. Resonate the shared purpose with your workforce and give them the sense of autonomy to design their own actions to achieve the larger goal.
In the end, it’s up to each organization to evaluate what's most suitable for them in terms of their culture, industry, and overall purpose. But, with employee autonomy, employees have better well-being and are more willing to work.
Are you willing to improve autonomy within teams? Ask your employees the degree of autonomy they require to excel through Culture Monkey’s anonymous employee experience surveys and receive actionable insights in real-time and take swift actions that create maximum impact.
FAQs
1. What is meant by "lack of autonomy" in the workplace?
"Lack of autonomy" in the workplace refers to situations where employees have limited freedom to make decisions, take initiative, or control their work processes. When employees lack autonomy, they may feel constrained by rigid rules and procedures, leading to a sense of powerlessness and frustration in their roles, ultimately impacting morale and productivity.
2. How does a lack of autonomy impact employee morale and job satisfaction?
A lack of autonomy can significantly impact employee morale and job satisfaction. Employees who feel micromanaged or restricted in their decision-making may experience decreased motivation and engagement. Without the freedom to contribute ideas, take ownership of tasks, and control their work processes, employees may feel undervalued and disengaged, ultimately affecting their overall satisfaction with their job.
3. How can organizations measure and assess the level of autonomy within their teams?
Organizations can measure and assess the level of autonomy within their teams through various methods, such as surveys, interviews, and performance evaluations. These assessments can include questions about decision-making authority, flexibility in work processes, and opportunities for initiative and creativity. By gathering feedback from employees and evaluating organizational policies and practices, organizations can gain insights into the level of autonomy present within their teams.
4. Can a lack of autonomy lead to feelings of frustration and disengagement among employees?
Yes, a lack of autonomy can indeed lead to feelings of frustration and disengagement among employees. When individuals feel stifled or micromanaged in their roles, they may become demotivated and disillusioned with their work. Without the ability to make meaningful contributions or take ownership of their tasks, employees may lose interest in their job and become disengaged from their work and the organization as a whole.
5. Does micromanagement contribute to a lack of autonomy in the workplace?
Micromanagement is a significant contributor to a lack of autonomy in the workplace. When managers excessively monitor and control employees' tasks and decisions, it undermines trust and autonomy within the team. Employees may feel disempowered and demoralized when their every move is scrutinized, leading to decreased morale and job satisfaction. Effective leadership involves trusting employees to perform their duties competently and allowing them the autonomy to do so.



