Autonomy in the workplace: Why is it important and relevant survey questions to ask in 2025?

Imagine a football game. Once the players are on the field, the coach can’t direct every move—they’re relying on the team to read the game, make quick decisions, and trust each other to make the right play.
Each player has a clear role but the freedom to adapt as the game unfolds, whether it’s calling an audible, adjusting a route, or spotting an opening. This autonomy on the field isn’t just crucial; it’s what drives those game-winning moments.
In the workplace, autonomy works the same way. When employees are empowered to make decisions and own their tasks, they’re not waiting for instructions; they’re actively driving toward the company’s goals. In this article, we’ll explore how autonomy can turn a team into a high-performing, self-motivated powerhouse, just like a winning football squad.
Blog Highlights


What is autonomy in the workplace?

Autonomy in the workplace means giving employees the freedom and responsibility to manage their own tasks, make decisions, and organize their work processes without constant oversight. This approach empowers individuals to leverage their strengths, use their judgment, and develop creative solutions.
Autonomy doesn’t mean working in isolation or disregarding company goals; rather, it involves aligning personal tasks with organizational objectives while trusting employees to determine how they accomplish these goals.
Workplace autonomy often leads to to higher job satisfaction, as it provides a sense of ownership and encourages personal growth. It also fosters innovation, as employees feel more encouraged to experiment and explore new ideas.
For autonomy to be effective, it requires a foundation of trust, clear communication, and well-defined expectations. Organizations that support autonomy typically benefit from increased employee engagement, productivity, and retention, as individuals feel more valued and motivated to contribute meaningfully to their work.
Workplace autonomy: What it is — and isn’t
Workplace autonomy is a cornerstone of modern organizational success, empowering employees with decision-making capabilities while maintaining alignment with company goals. However, misconceptions about its scope often lead to misapplication. Understanding what workplace autonomy is — and isn’t — helps foster an autonomous environment.
What workplace autonomy is:
- Aligned independence: Employees have the freedom to decide how they execute tasks and make their own decision while adhering to organizational priorities. This ensures creativity without deviating from company objectives.
- Skill-based decision-making: Employees leverage their expertise, boosting job performance and motivation. Granting autonomy this way also promotes skill development across the organization.
- Collaborative flexibility: Autonomy thrives on mutual trust and open communication, encouraging collaboration while respecting unique approaches to work.
- A driver of accountability: By giving employees greater control, workplace autonomy increases responsibility, creating a high-performance culture.



Human beings have an innate inner drive to be autonomous, self-determined, and connected to one another. And when that drive is liberated, people achieve more and live richer lives.
Author
What workplace autonomy isn’t:
- Complete independence: Employee autonomy doesn’t mean disregarding team goals or company guidelines. Instead, it allows employees to take ownership of their processes within set boundaries.
- Absence of oversight: Managers still provide guidance, mentorship, and the right tools to ensure employee engagement aligns with business objectives.
- One-size-fits-all: Autonomy is flexible, varying across roles and capabilities, ensuring employees feel supported while taking on more responsibility.
How does workplace autonomy differ from personal autonomy?
Workplace autonomy and personal autonomy share the foundation of freedom and self-governance, yet they operate in distinct contexts with unique implications. While both involve decision-making and independence, their application and impact vary significantly.
Workplace autonomy is structured within organizational frameworks. It involves granting employees the freedom to decide how they accomplish tasks, manage responsibilities, and contribute to team goals. However, this autonomy exists within the boundaries of company policies, shared objectives, and collaborative efforts, ensuring alignment with organizational priorities.
Personal autonomy, on the other hand, is self-directed and uninfluenced by external frameworks. It revolves around decisions that impact an individual’s personal life, values, and aspirations, without the need to align with organizational goals or collaborative efforts.
In essence, autonomy in the workplace balances personal freedom with collective objectives, while personal autonomy emphasizes individual control. Both are essential, but workplace autonomy integrates structure and collaboration to ensure the entire workforce thrives within shared priorities.
Why is autonomy in the workplace important?
Autonomy in the workplace empowers employees to make decisions, fueling motivation and innovation. Here’s how it transforms both individual and organizational success.
- Boosts motivation and engagement: Autonomy gives employees the freedom to make decisions and take ownership of their work, enhancing their sense of purpose. They’re not just clocking hours—they’re actively contributing to meaningful goals, which drives them to strive for excellence and take pride in their achievements.
- Encourages creativity and innovation: When employees have room to explore and experiment, they’re more likely to think outside the box. This freedom to innovate leads to new ideas, breakthroughs, and an environment where every employee's unique perspectives contribute to growth.
- Builds trust and collaboration: In an autonomous culture, employees are trusted to make decisions and manage responsibilities. This trust fosters mutual respect, transforming managers into mentors who guide rather than micromanage, which strengthens team collaboration.
- Enhances skill development: Autonomy allows individuals to tackle new challenges, broadening their skill sets. This freedom to grow supports continuous learning and empowers employees to shape their own career paths.
- Promotes personal and professional fulfillment: By enabling growth and learning, autonomy serves as a catalyst for both personal satisfaction and career advancement, giving employees a sense of fulfillment in their roles.
Types of autonomy in the workplace
Autonomy in the workplace can take on different forms, each tailored to support various work styles and environments. By recognizing and implementing these types, companies can empower employees to work in ways that best suit their strengths and responsibilities.
- Task autonomy: Employees have control over how they complete assigned tasks, selecting their methods and approaches independently. This freedom fosters creativity and encourages employees to find innovative solutions.
- Time autonomy: Employees can decide when they work, allowing them to align their hours with personal productivity peaks. This flexibility can reduce burnout and improve focus, especially valuable in remote or flexible work settings.
- Role autonomy: Team members have input in shaping their roles, selecting projects or areas that align with their skills and interests. Role autonomy enhances motivation, as employees are more engaged when they work on tasks that resonate with their strengths.
- Goal autonomy: Employees are involved in setting goals and priorities, giving them a stake in the outcomes. This sense of ownership boosts accountability, driving individuals to meet objectives with greater commitment.
9 Benefits of autonomy in the workplace

- Supercharged motivation: Autonomy is like a magic potion for employee motivation. When employees are free to make decisions and take ownership of their work, their motivation skyrockets. They become driven by a sense of purpose and a desire to excel. Say goodbye to those dreary Monday mornings and hello to a workforce brimming with passion and enthusiasm.
- Unleashed creativity: Creativity is one of the top perks of autonomy. When individuals have the freedom to explore, experiment, and unleash their imaginations, fresh ideas flow, and creative breakthroughs become the norm. Who needs a creativity workshop when you've got autonomy fueling the fire?
- Trust and empowerment: It builds trust between employees and managers. When individuals are trusted to make decisions and take responsibility, they feel empowered. Managers become mentors, guiding and supporting their teams rather than breathing down their necks.
- Enhanced collaboration: Autonomy and collaboration go hand in hand. When employees have the freedom to bring their unique perspectives to the table, teamwork soars. Ideas are shared, diverse talents are harnessed, and synergy becomes the secret sauce that propels organizations forward. It's like a jam session where everyone gets a chance to shine.
- Increased job satisfaction: Employees who are given control over how they manage their work are more satisfied with their job. Autonomy transforms work into a fulfilling and meaningful experience, leaving employees with smiles on their faces and pep in their steps.
- Personal and professional growth: Autonomy is a springboard for growth. When employees learn, take on new challenges, and shape their own career paths, they blossom. They acquire new skills, expand their horizons, and become their best selves.
- Agility and adaptability: When employees make decisions on the spot, they become nimble and adaptable. They can respond swiftly to changing circumstances and seize opportunities without waiting for approvals from higher-ups.
- Reduced burnout: Autonomy acts as a shield against burnout. Employees that have control over their workload, priorities, and pace find balance. They have the power to set boundaries, take breaks when needed, and align their work with their energy levels.
- Attraction and retention of top talent: An autonomous company culture is a magnet for top talent. In a world where talented individuals seek meaningful work and a sense of purpose, autonomy stands out. Organizations that embrace autonomy become beacons for the best and brightest.
Disadvantages of autonomy in the workplace
While autonomy can bring numerous benefits, there are potential disadvantages when it’s not managed effectively:
- Inconsistent results: With high levels of autonomy, employees may adopt differing methods, leading to inconsistent outcomes that impact quality and brand reputation.
- Difficulty in coordination: When individuals or teams operate independently, it can create silos, making it challenging to align on goals and coordinate efforts, especially on cross-functional projects.
- Decision-making overload: Too much autonomy can overwhelm employees who may not feel equipped to make constant decisions, potentially leading to stress or decision fatigue.
- Risk of reduced accountability: In highly autonomous environments, the line between individual and team accountability can blur, making it harder to identify and address performance issues.
- Potential for inefficiency: Without structured oversight, autonomous employees may invest time in tasks that don’t align with company priorities, potentially reducing overall efficiency.
Empowerment, autonomy and authority
Empowerment, autonomy, and authority each play distinct roles in workplace dynamics:
| Aspect | Empowerment | Autonomy | Authority |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Providing employees with resources and support to achieve their potential | Granting freedom to make choices in how tasks are executed | Enabling individuals to make decisions that impact the organization |
| Scope | Focuses on skill development and growth opportunities | Emphasizes task ownership and flexibility | Encompasses setting objectives and enforcing policies |
| Impact | Builds confidence and fosters a proactive mindset | Encourages creativity and innovation | Ensures accountability and alignment with strategic goals |
| Employee role | Actively engage in learning and skill-building | Choose methods and schedules to achieve tasks effectively | Make critical decisions that guide team or project outcomes |
| Manager’s role | Support through mentorship and development resources | Trust employees to manage their own processes | Oversee and guide alignment with broader organizational strategy |
Levels of autonomy at work
Autonomy at work exists on a spectrum, with different levels to suit varying roles and team needs:
- Basic autonomy: Employees complete tasks independently but follow defined processes under close supervision. This level is ideal for new hires or roles requiring structured workflows.
- Moderate autonomy: Workers have flexibility in how they approach tasks within set guidelines, allowing some room for creativity and adaptation. This level helps build confidence in decision-making while still providing a safety net.
- High autonomy: Employees set their priorities, manage projects, and make key decisions that align with team goals, with minimal oversight. This level fosters accountability and innovation, particularly in experienced teams.
- Complete autonomy: Team members control the project’s direction, decisions, and resources, holding full accountability for outcomes. Complete autonomy suits highly skilled teams working in complex or creative environments.
- Strategic autonomy: Employees have the freedom to propose new projects and long-term goals, contributing to the company’s vision and strategy. This top-tier level empowers trusted employees to lead growth and innovation initiatives, shaping the organization’s future.



The key element of engagement is trust; building trust requires companies to provide workers with as much autonomy and flexibility as possible.
Editor in Chief
Recruiter.com
How autonomy differs from flexibility and remote working?
Autonomy, flexibility, and remote working are often used interchangeably, but each serves a unique purpose in the workplace:
| Aspect | Autonomy | Flexibility | Remote working |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Grants employees control over how they complete their tasks, with decision-making power in their roles | Allows employees to adjust their schedules or work hours, offering freedom within structured guidelines | Enables employees to work outside the traditional office setting, often from home or other locations |
| Scope | Focused on task management, decision-making, and ownership of outcomes | Centered on adaptable working hours or custom schedules | Primarily concerns the location of work rather than how tasks are done |
| Impact on work style | Encourages innovation and independence, as employees are trusted to determine their methods and approaches | Supports work-life balance by letting employees manage personal and professional commitments | Enhances convenience and reduces commuting, potentially increasing productivity in suitable roles |
| Manager's role | Provide guidance but allow employees freedom in their approaches to work | Set boundaries and expectations while allowing flexible hours | Establish clear communication channels and expectations for remote team members |
| Examples | Task-based project ownership, self-directed goal setting | Choosing start/end times, compressed work weeks | Working from home, coworking spaces, or on a hybrid basis |
Lack of autonomy in the workplace
A lack of autonomy in the workplace can result in a restrictive, disengaged environment. Here are some key issues that arise:
- Micromanagement: Excessive oversight stifles creativity and discourages independent problem-solving, leading to frustration and diminished morale.
- Limited flexibility: Rigid schedules and strict processes hinder employees from adapting work methods, impacting productivity and satisfaction.
- Low accountability: When decision-making is centralized, employees feel disconnected from outcomes, reducing motivation.
- High turnover: An inflexible work culture often leads to increased employee turnover as workers seek environments with greater freedom and trust.
- Reduced innovation: Without the freedom to explore new ideas or take initiative, employees are less likely to contribute innovative solutions, which can hinder the organization's growth and adaptability in a competitive market.
- Stress and burnout: Constant oversight and lack of control over work processes can increase stress, as employees may feel pressured to meet unrealistic expectations or work within limiting frameworks, leading to burnout over time.
- Decreased skill development: When tasks and methods are rigidly defined, employees have fewer opportunities to expand their skills, try new approaches, or build confidence in decision-making, limiting their professional growth and career satisfaction.
How to implement autonomy in the workplace?

Implementing autonomy in the workplace empowers employees and drives meaningful engagement. Here are key steps to fostering a culture of autonomy in your organization:
- Set clear expectations: Begin by defining goals and objectives so employees understand their roles and how their contributions impact organizational success. As Ken Blanchard notes, clarity in expectations is key to achieving desired outcomes.
- Encourage open communication: Create a culture where ideas and feedback flow freely. Leadership should facilitate opportunities for employees to share opinions and insights, fostering a collaborative environment.
- Empower decision-making: Allow employees to take ownership by involving them in decision-making processes. This trust strengthens their commitment to their roles and builds confidence.
- Provide necessary resources: Ensure employees have the tools, training, and support needed to succeed. Offering resources helps them perform autonomously while meeting organizational goals.
- Foster a culture of growth: Embrace successes and failures as learning opportunities. As J.K. Rowling said, "It is impossible to live without failing at something," underscoring that growth often comes from risks.
- Build trust gradually: Autonomy takes time to flourish. With patience, trust, and encouragement, you’ll create an environment where autonomy becomes the norm.
- Train managers: Equip managers with skills to foster autonomy by balancing guidance and independence, promoting mutual trust and effective decision-making.

Create an Empowered Workplace
with Autonomy
Discover actionable steps to effectively implement workplace autonomy and achieve organizational goals.
What are examples of autonomy in the workplace?

Examples of autonomy in the workplace show how empowering employees to take ownership of their work can lead to creative and meaningful outcomes. Here are some key examples:
- Project ownership: Employees are given full responsibility for managing a project from start to finish, including setting goals, making decisions, and solving problems independently. For instance, a team member in product development might lead the design and execution of a new feature, taking full ownership of the process.
- Flexible scheduling: Workers decide when they perform their tasks, allowing them to work during their most productive hours. A writer, for example, might choose to draft content early in the morning or late at night, depending on when they feel most creative.
- Creative freedom in strategy: Marketing teams are often allowed to brainstorm and experiment with new campaign ideas. A social media specialist, for instance, might develop a unique engagement strategy involving user-generated content, fostering direct interaction with followers.
- Decision-making in task execution: Employees are trusted to choose their own methods for completing tasks. A software developer could select the programming languages and tools they feel will work best for building an app feature, based on their expertise.
- Goal setting: Teams or individuals participate in setting their own objectives, aligning personal goals with company targets. Sales teams, for example, might set monthly targets for client outreach or revenue based on current market trends.
- Innovation through experimentation: Employees are encouraged to try new approaches. A content creator might test different video formats and engagement styles, refining their strategy based on metrics and feedback.
- Collaborative autonomy: Autonomy allows team members to brainstorm, collaborate, and adjust plans as needed. For example, a product design team could share ideas freely, adjusting the prototype vs MVP approach based on each designer’s input and feedback.
Autonomy and well-being
Autonomy in the workplace is like the roots of a tree—providing stability and nourishment for growth while allowing flexibility to adapt. When employees feel empowered to work independently, their well-being flourishes, benefiting the entire workforce.
Workplace autonomy improves workplace mental health by reducing stress and burnout. Employees who feel trusted to make their own decisions are more likely to experience job satisfaction and mental clarity.
Autonomy also promotes work life harmony. Employees with flexibility to manage their own schedules are better equipped to balance personal boundaries and work responsibilities, fostering physical and emotional resilience.
Moreover, autonomy enhances collaboration and creative thinking. Employees thrive in an environment that encourages mutual trust and values their unique contributions, resulting in a happier, healthier workforce. In essence, autonomy creates psychological safety, supporting emotional, physical, and social dimensions of well-being.
How to nurture autonomy in different work environments
Nurturing autonomy across different work environments requires thoughtful strategies tailored to each team’s needs. To nurture autonomy effectively, it’s essential to adapt strategies to remote, hybrid, and in-person work settings.
Remote work
- Empower self-management: Provide remote employees with tools and resources to manage their schedules. Clear expectations and flexibility encourage a sense of ownership.
- Foster transparent communication: Regularly share company goals and project updates so remote teams feel connected and confident in decision-making.
- Encourage outcome-based goals: Focus on results rather than hours worked. This flexibility allows employees to choose their most productive work methods and times.
Hybrid work
- Define in-office and remote autonomy: Allow hybrid employees to choose tasks for remote or in-office days. Giving them control over these decisions fosters a stronger sense of ownership.
- Use collaborative tech: Invest in shared tools like project management apps to help hybrid teams work independently while staying connected with in-office and remote colleagues.
- Promote self-directed skill development: Encourage hybrid employees to use office time for peer learning and remote time for focused skill-building, giving them autonomy over growth.
In-person work
- Create independent task zones: Designate quiet spaces or ‘task zones’ where in-person teams can work independently, enhancing focus and self-guided work.
- Implement peer-led projects: Let employees lead small group projects or initiatives, allowing them the freedom to make decisions and innovate.
- Empower role rotation: Allow team members to rotate tasks within their departments, which fosters versatility and gives them autonomy in choosing responsibilities they want to explore.
How do you measure autonomy in the workplace?

Measuring workplace autonomy can be tricky, as it is a subjective and nuanced concept. However, there are a few key indicators that can help gauge the level of autonomy within an organization:
- Employee surveys: Conducting anonymous surveys can provide valuable insights into employees' perceptions of autonomy. Ask questions about decision-making authority, freedom to choose work methods, and the level of control they feel over their own work.
- Feedback and performance reviews: Assessing feedback and performance reviews can provide clues about the level of autonomy employees have. Are they encouraged to take the initiative and make independent decisions? Do their reviews emphasize autonomy-related skills like problem-solving and decision-making? This will give you a clear idea of organizational autonomy.
- Project ownership: Look at how employees approach and take ownership of their projects. Are they given the flexibility to explore alternative approaches and problem-solving methods? Observing how employees handle project ownership can indicate their autonomy level within their roles.
- Employee retention and engagement: High levels of autonomy often correlate with increased retention and engagement. If employees feel empowered and have control over their work, they are more likely to be engaged and committed to their roles.
50+ Questions about autonomy in the workplace you should be asking

Asking the right questions in an engagement survey based on your objective is key to gaining actionable insights. So, we have compiled 50+ questions that you should be asking in your workplace to gauge the level of employee autonomy the organization has.
- Describe a situation where you felt empowered to make decisions in your work.
- Share an example of when you were given employee autonomy to take ownership of a project or task.
- Do you have the freedom to choose how you approach and complete your tasks?
- Are you involved in the decision-making process that directly affects your work?
- Are you provided with the necessary resources and support to work autonomously?
- Do you feel comfortable suggesting improvements or changes to processes?
- On a scale of 1-5, how much autonomy do you feel you have in your day-to-day work?
- Have you been given opportunities to develop and apply your own ideas in your work?
- Please describe a recent instance where you felt supported in making an important decision.
- Rate your satisfaction with your current level of autonomy in your role.
- Are you recognized and rewarded for taking ownership and demonstrating autonomy?
- Are you encouraged to take calculated risks and learn from mistakes?
- Is there room for experimentation and innovation within your role?
- Are you provided with the necessary resources and support to work autonomously?
- Do you feel trusted to prioritize and manage your own workload?
- Is your manager trusting or do they micromanage every single task?
- Do you have a clear understanding of the expectations and boundaries within your role?
- Do you have the flexibility to adjust your working hours to align with your peak productivity times?
- Are you given opportunities to set personal goals that align with the organization’s objectives?
- How often do you receive feedback that encourages independence rather than detailed instructions?
- Are you encouraged to pursue professional development opportunities that align with your career goals?
- Do you feel that your input is valued when team strategies and goals are set?
- Are you allowed to choose which tools or methods you use to complete your tasks effectively?
- Is your performance evaluated based on results rather than the specific steps you take?
- How confident are you that your manager supports your decisions, even if they involve some calculated risks?
- Do you have regular one-on-one meetings where you can discuss your preferences for autonomy in your role?
- Are you encouraged to explore innovative approaches to solve problems within your projects or tasks?
- How often are you asked for your input on team or project decisions?
- Are you given the opportunity to delegate tasks or responsibilities within your team?
- Do you feel empowered to resolve conflicts or challenges on your own?
- Are you encouraged to prioritize your workload based on what you feel is most impactful?
- How often do you receive training on managing autonomy effectively?
- Are you given the freedom to propose new projects or initiatives?
- Do you feel your role provides enough flexibility to balance work with personal life demands?
- Are you involved in setting deadlines for your tasks or projects?
- How much freedom do you have to adjust your work processes when faced with unexpected challenges?
- Do you feel you can voice concerns about your level of autonomy without fear of repercussions?
- Are you encouraged to take ownership of cross-functional projects?
- How often do you receive feedback on your independent decision-making abilities?
- Do you feel your team collaborates effectively while allowing individual autonomy?
- Are you trusted to handle client or stakeholder interactions independently?
- Have you been given opportunities to lead a project or team?
- Do you feel autonomy has positively impacted your productivity and job satisfaction?
- How often do you engage in brainstorming sessions where your ideas are implemented?
- Are you given freedom to select tools or platforms that help you work more efficiently?
- Do you feel your autonomy level aligns with your role and responsibilities?
- Are you encouraged to set personal development goals as part of your professional growth?
- Do you feel the organization provides sufficient support to foster autonomy in your role?
- Are you allowed to experiment with different approaches to improve efficiency in your work?
- Do you have the freedom to take breaks or adjust your schedule to improve focus and energy?
- Are team decisions transparent enough to allow you to align your autonomous tasks effectively?
- How well do you feel your manager balances autonomy with oversight?

Enhance Workplace Satisfaction with Autonomy Surveys
Gain actionable insights with 20 autonomy-focused survey questions designed to drive engagement and boost workplace success.
How do you promote autonomy in the workplace?

Enabling employee autonomy in the workplace requires intentional efforts and a supportive environment. Here are some key strategies to encourage autonomy in your organization:
- Clearly define goals and expectations: Set clear goals and expectations for each employee, providing them with a clear understanding of what needs to be achieved. Clarify the purpose and impact of their work, allowing them to see the bigger picture and align their efforts accordingly.
- Delegate responsibility: Delegate tasks and responsibilities to employees, allowing them to take ownership and make decisions within their areas of expertise. Provide them with the authority and autonomy to execute their work while being available for guidance and support when needed.
- Encourage independent thinking: Foster a culture that values independent thinking and encourages employees to explore new ideas and perspectives. Encourage them to question the status quo, challenge assumptions, and contribute their unique insights.
- Provide resources and support: Ensure that employees have the necessary resources, tools, and training to excel in their roles. Support their professional growth and development through mentoring, in-person or personalized online coaching, and relevant learning opportunities. This empowers them to take on new challenges with confidence.
- Foster collaboration and communication: Promote collaboration and open communication channels within the organization. Encourage employees to share their thoughts, ideas, and concerns openly. Create a safe space where individuals can discuss their work, provide feedback, and collaborate with their peers.
- Recognize and celebrate autonomy: Acknowledge and appreciate employees who demonstrate autonomy in their work. Recognize their accomplishments and efforts, both privately and publicly. Celebrate their leadership qualities, independent thinking, and decision-making abilities, reinforcing the importance and value of autonomy in the workplace.
- Embrace a learning culture: Cultivate a learning culture that encourages continuous improvement and experimentation. Encourage employees to learn from both successes and failures, allowing them to take calculated risks and grow from their experiences.
Myths about workplace autonomy: what leaders need to know

Workplace autonomy is often misunderstood, like a misunderstood orchestra—where freedom to play doesn’t mean chaos, but harmony under a shared vision. While autonomy is a powerful tool for engagement, misconceptions can lead to ineffective implementation. Leaders must debunk these myths to create a balanced and productive autonomous environment.
- Autonomy means no oversight: Autonomy doesn’t equate to an absence of management. Leaders still need to provide guidance, clear objectives, and support to ensure employees align their independence with organizational goals.
- Everyone wants full autonomy: Not all employees thrive under high autonomy. Some prefer structured environments with clear instructions and expectations, making it essential to tailor autonomy levels to individual needs and roles.
- Autonomy hinders teamwork: A common myth is that autonomy isolates employees. In reality, autonomy can enhance collaboration by empowering individuals to bring unique ideas to the table, enriching team discussions and outcomes.
- Autonomy guarantees instant results: Building an autonomous work culture takes time and effort. Employees need training, trust, and a supportive environment to fully leverage their independence for meaningful contributions.
- Autonomy replaces accountability: Autonomy doesn’t absolve employees of accountability. Instead, it strengthens responsibility by making individuals answerable for their decisions and outcomes, which drives better performance.
How does autonomy in the workplace impact employee engagement?

Encouraging autonomy in the workplace has a significant impact on employee engagement. Here are some ways emploee autonomy effect engagement in an organization.
- Increased motivation: Autonomy fosters intrinsic motivation as employees feel a sense of empowerment and control over their work.
- Improved job satisfaction: When individuals can exercise their judgment, be creative, and contribute their unique perspectives, they feel a deeper connection to their work and derive more satisfaction from their accomplishments.
- Enhanced sense of ownership: Employees who feel trusted and empowered to make decisions develop a stronger sense of responsibility and commitment to achieving their goals. This ownership mindset fuels engagement and a desire to excel.
- Greater sense of purpose: Autonomy connects employees' work to a larger purpose. When they align their tasks with their personal values and aspirations, they experience a deeper sense of meaning and fulfillment. This alignment enhances their engagement and dedication to their work.
- Increased creativity and innovation: Autonomy fosters a culture of creativity and innovation. Employees who freely explore new ideas, experiment, and take calculated risks, are more likely to generate innovative solutions and contribute fresh perspectives.
- Strengthened trust and collaboration: When individuals are given the autonomy to make decisions, it signals trust and confidence in their abilities. This trust enhances collaboration, as employees feel valued and empowered to contribute their expertise and perspectives.
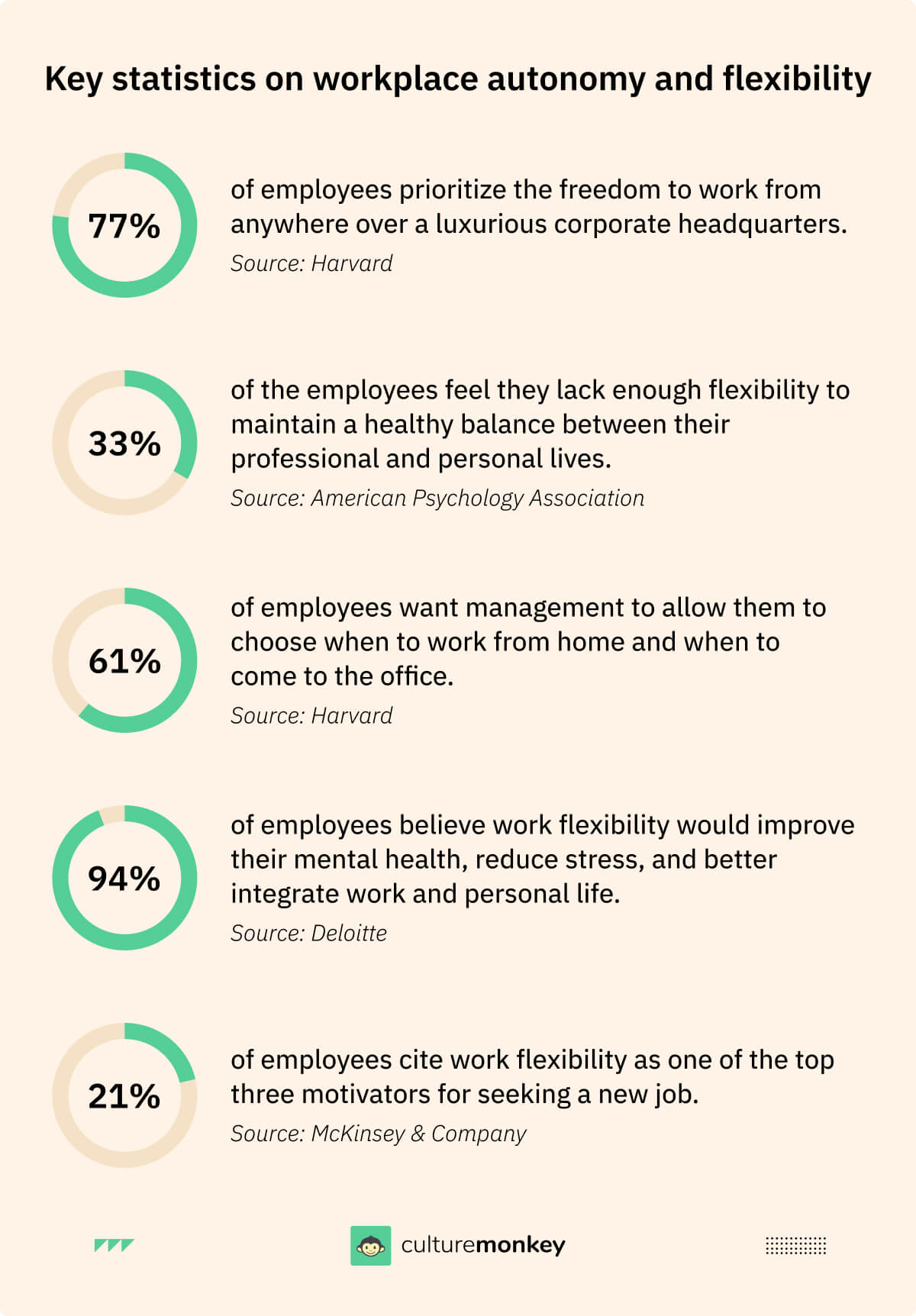
How to improve and sustain autonomy in the workplace with the help of employee survey tools?

To improve and sustain autonomy in the workplace, follow these steps:
- Set clear goals and expectations to give employees a solid understanding of their responsibilities and objectives.
- Build open communication channels to encourage regular feedback and idea-sharing, creating a collaborative atmosphere that supports autonomy.
- Provide decision-making opportunities, empowering employees to make choices related to their projects, which fosters independence and accountability.
- Ensure employees have access to the necessary resources and training, equipping them with the tools and skills for autonomous work.
- Balance freedom with accountability to keep projects on track and maintain focus on the team’s objectives.
- Celebrate both successes and setbacks as growth opportunities, recognizing efforts regardless of outcomes, to create a culture that values learning and thoughtful risk-taking.
Build autonomy in workplace with CultureMonkey
Creating autonomy in the workplace requires more than just policies—it demands tools that empower, engage, and provide actionable insights. CultureMonkey offers the perfect solution to foster an autonomous work environment tailored to your organization’s needs.
Heatmap visualisation
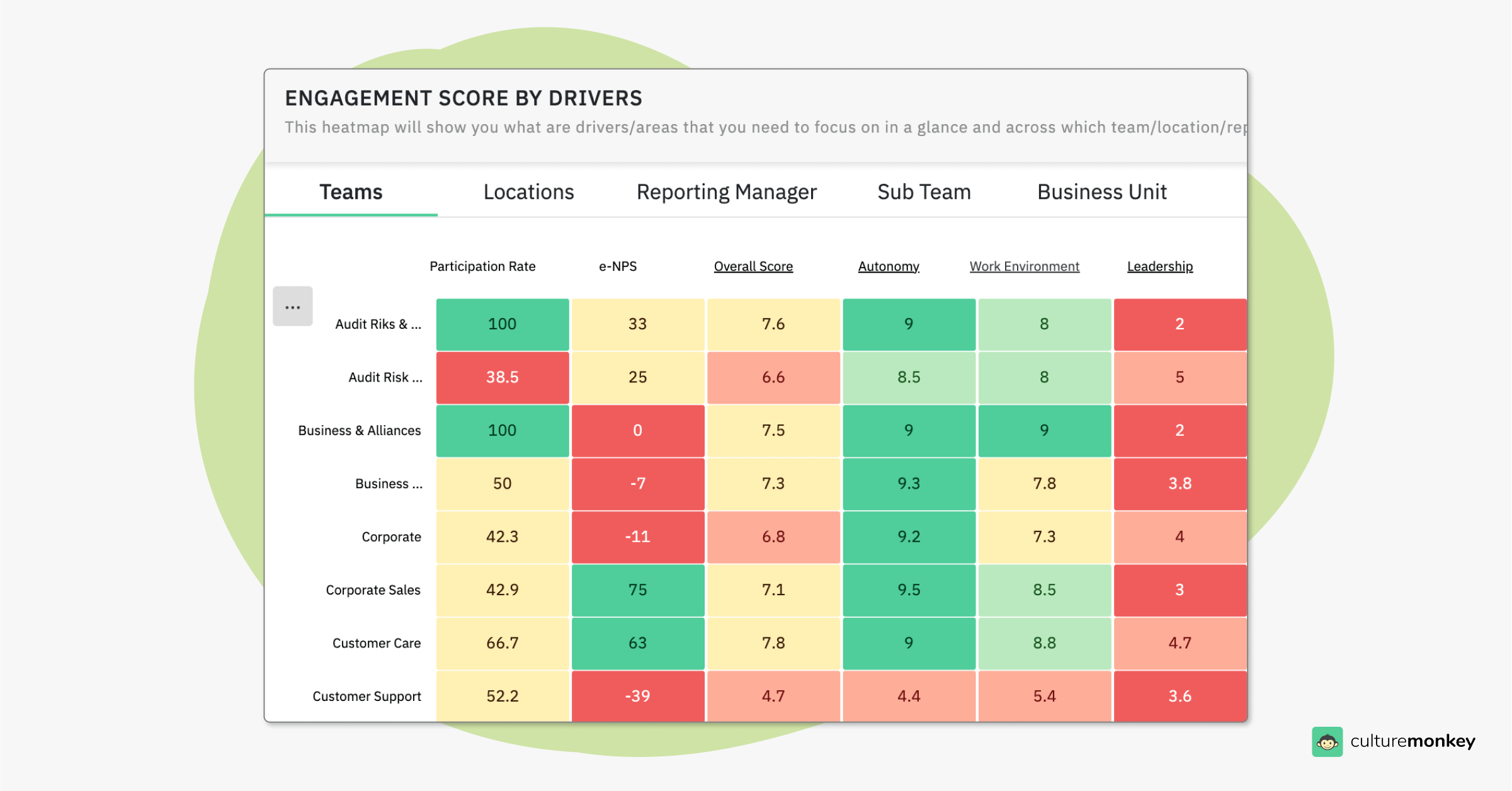
With CultureMonkey's heatmap visualization, managers gain clear insights into how autonomy is distributed across different teams or departments. This feature makes it easy to identify areas where employees feel empowered versus where they need more independence, enabling targeted actions that foster greater workplace autonomy.
Customisable autonomy survey templates
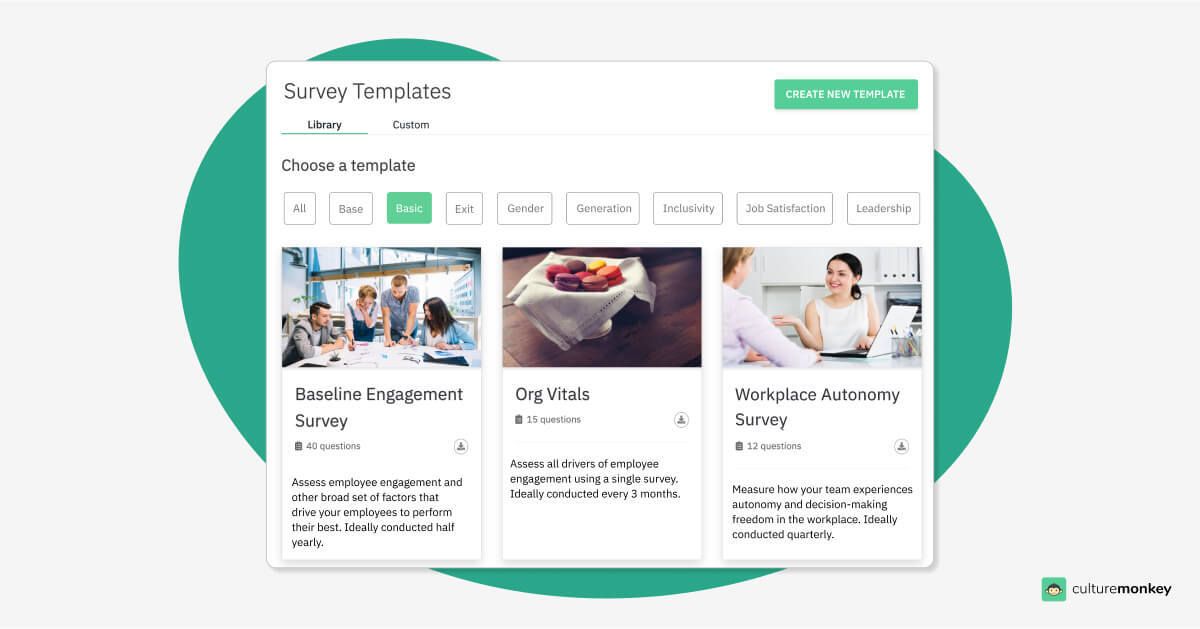
CultureMonkey offers customizable autonomy survey templates allow organizations to tailor questions specifically around workplace autonomy. This flexibility ensures that surveys reflect the unique needs and culture of your company, leading to actionable insights that truly resonate with employees and support their autonomy journey.
Built-in Likert scale
The built-in Likert scale provides employees with an easy and intuitive way to express their feelings about autonomy levels. By quantifying these perceptions, CultureMonkey helps you measure workplace autonomy effectively, making it possible to track progress and improve areas that matter most.
Sentiment analysis tools
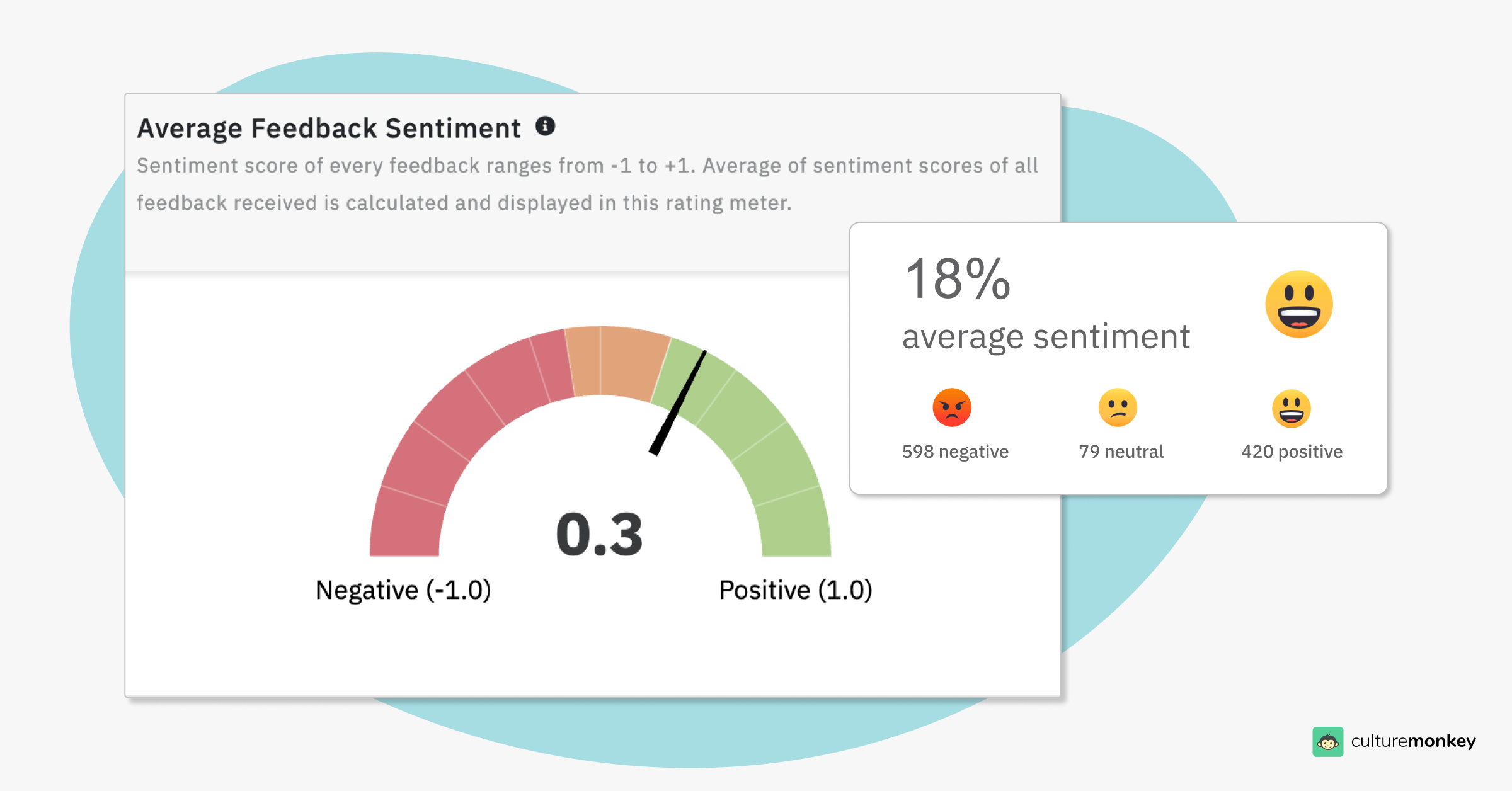
CultureMonkey’s sentiment analysis tools capture how employees feel about the freedom and flexibility in their roles. By analyzing feedback, HR leaders can gauge levels of autonomy within teams, identifying areas where employees feel empowered and where adjustments are needed to provide greater independence, ultimately fostering a supportive and flexible work culture.
Action recommendations

Personalized recommendations that guide managers and leaders on practical next steps to enhance autonomy. These targeted actions empower teams, build trust, and create a culture where employees enjoy the independence they need to thrive. With CultureMonkey, autonomy evolves from an idea into measurable success.
Conclusion
Workplace autonomy is essential for fostering innovation, enhancing employee satisfaction, and driving organizational success. It empowers individuals to take ownership of their roles, unleashing creativity and accountability. By building a culture of trust and providing employees with the freedom to make decisions, organizations can achieve greater engagement and productivity.
Embracing autonomy isn’t just a strategy—it’s a cornerstone for sustainable growth and a thriving workplace. As important autonomy sounds for an organization, it is essential to measure and improve it. This is where an employee engagement survey software like CultureMonkey saves the day.
CultureMonkey helps you to seamlessly send employee autonomy surveys to your team members across geographies, to accurately measure, analyze and improve your workplace autonomy, without breaking a sweat. Book a demo with us today!
Summary
Workplace autonomy empowers employees to make decisions, boosting engagement, innovation, and accountability. It balances freedom with collaboration, fostering trust and responsibility. Implementing autonomy requires clear goals, resources, and supportive leadership while addressing common myths. By encouraging independent thinking, celebrating achievements, and promoting a learning culture, autonomy enhances well-being, productivity, and overall organizational success.
FAQs
1. How does autonomy in the workplace impact retention of employees?
When employees have a sense of autonomy and control over their work, they feel more engaged, satisfied, and fulfilled. This increased job satisfaction and motivation can contribute to higher employee retention rates, enhanced productivity, and a positive workplace culture where individuals are empowered to take initiative and innovate. Autonomy fosters commitment, making employees more likely to grow and develop within the organization.
2. Is autonomy in the workplace a good thing?
Yes, autonomy is highly beneficial in the workplace. It empowers employees to take ownership of their roles, which increases engagement and motivation. With autonomy, employees are more likely to bring creativity and innovation to their tasks, as they feel trusted and valued. This sense of responsibility often leads to higher productivity, job satisfaction, and commitment, creating a more effective and dynamic workplace overall.
3. How does autonomy in job design affect employees?
Autonomy in job design allows employees to shape their roles based on their skills and interests, increasing motivation and job satisfaction. This freedom can reduce burnout by enabling individuals to work in ways that align with their strengths. When employees have the flexibility to manage their responsibilities, they feel more valued, leading to better performance and a greater sense of purpose in their work.
4. How much freedom do you give employees, and how do you provide this freedom while maintaining authority?
Providing balanced freedom involves allowing employees to make task-related decisions while setting clear goals and expectations. This balance is achieved by conducting regular check-ins and offering guidance when needed. By focusing on outcomes rather than micromanaging processes, managers can maintain authority and alignment with company objectives while encouraging employees to work independently, fostering both accountability and trust.
5. What does autonomy in the workplace look like?
Autonomy in the workplace allows employees to control how they complete their tasks. It means they’re empowered to make decisions about their workflows, schedules, and problem-solving approaches, contributing unique perspectives to their roles. They take responsibility for achieving outcomes, while managers act as supportive guides. Autonomy encourages collaboration and creativity, as employees are trusted to drive their own success within team goals.




