What is an employee engagement score? What does a good score look like?

In 2014, Microsoft underwent a major cultural transformation under CEO Satya Nadella. The company shifted its focus from a "know-it-all" culture to a "learn-it-all" mindset, emphasizing employee growth and collaboration. A critical part of this shift? Listening to employee feedback and prioritizing their satisfaction.
Microsoft began using data-driven tools and regular surveys to measure how employees felt about their work environment. The result? Increased innovation, improved teamwork, and a resurgence that made Microsoft one of the most valuable companies in the world.
This kind of success isn’t accidental—centered on understanding and enhancing the process of how to measure employee satisfaction score effectively. The employee engagement score is a powerful way to do just that, helping you create an environment where employees thrive and your company grows. Here’s how it works.
Blog Highlights


Why is employee engagement important?

Employee engagement is vital for organizations as it brings numerous benefits and contributes to overall success. Here are the key reasons why employee engagement is important:
- Increased productivity: Engaged employees are more motivated, committed, and focused on their work. They take ownership of their tasks, demonstrate higher levels of productivity, and consistently deliver high-quality results. They are driven to go the extra mile, leading to increased efficiency and effectiveness in their roles.
- Improved job satisfaction: When employees feel engaged, they experience higher levels of job satisfaction. They find fulfillment in their work, feel valued by the organization, and experience a sense of purpose and accomplishment. This satisfaction not only leads to more job security and increased employee happiness but also helps to retain top talent within the organization.
- Enhanced employee retention: Employee engagement plays a crucial role in retaining valuable talent. Engaged employees are more likely to stay committed to the organization and have a lower inclination to seek opportunities elsewhere. They feel connected to the organization's mission and values, have strong working relationships, and see opportunities for professional growth and development.
- Increased employee loyalty: Highly engaged employees develop a sense of loyalty and commitment to the organization. They feel invested in its success and are more likely to advocate for the organization both internally and externally. They become brand ambassadors, promoting a positive image of the organization to clients, customers, and potential hires.
- Improved collaboration and teamwork: Employee engagement fosters a collaborative work environment. Employees actively participate in team initiatives, share knowledge, and build positive relationships with team managers and senior leadership, leading to improved teamwork and cooperation within the organization.
- Enhanced innovation and creativity: Engaged employees are more likely to think creatively, offer innovative solutions, and take calculated risks. They create an environment that encourages innovation, leading to continuous improvement and a competitive edge for the organization.
- Better customer satisfaction: Engaged employees have a direct impact on customer satisfaction. They provide better service, demonstrate higher levels of empathy, and go above and beyond to meet customer needs. They understand the importance of customer satisfaction and actively work to deliver exceptional experiences, ultimately contributing to customer loyalty and business success.
- Positive organizational culture: Employee engagement contributes to a positive organizational culture. It promotes open communication, trust, and transparency. Employees feel comfortable voicing their opinions, collaborating across departments, and challenging the status quo. A positive culture attracts and retains top talent, fosters innovation, and strengthens the overall reputation of the organization.



Create caring and robust connections between every employee and their work, customers, leaders, managers, and the organization to achieve results that matter to everyone in this sentence.
David Zinger Associates
Why should you measure employee engagement in the first place?

- Identify strengths and areas for improvement: Provides insights into organizational strengths and weaknesses, helping focus efforts on areas that need attention to foster an engaging workplace.
- Enhance employee satisfaction score and retention: Gauges satisfaction levels, identifies drivers of loyalty, and enables proactive steps to improve engagement, retention, and reduce turnover costs.
- Drive performance and productivity: Correlates engagement levels with performance metrics, helping develop strategies to improve productivity through stronger engagement.
- Enhance decision-making and strategy development: Offers data-driven insights to evaluate policies and align strategies with employee needs for better organizational outcomes.
- Foster a culture of feedback and continuous improvement: Encourages regular feedback, demonstrating that employee opinions matter and fostering trust, transparency, and positive change.
- Support employee development and well-being: Identifies areas requiring additional support, promoting employee growth, satisfaction, career progression, and overall well-being.
What are the 3 key aspects of measuring employee engagement?

When measuring employee engagement, there are three key aspects that organizations should consider:
- Survey design and administration: Design surveys with clear, concise questions addressing job satisfaction, motivation, and commitment. Ensure anonymity to promote honest feedback. Administer surveys regularly to capture updated insights and track engagement trends.
- Data analysis and interpretation: Analyze survey data to identify trends, strengths, and improvement areas. Use statistical methods like correlation and factor analysis to uncover relationships. Proper interpretation leads to meaningful, actionable insights.
- Action planning and implementation: Develop targeted action plans based on survey findings, with clear goals and responsibilities. Communicate plans to employees, involve them in initiatives, and monitor progress to drive engagement improvements.
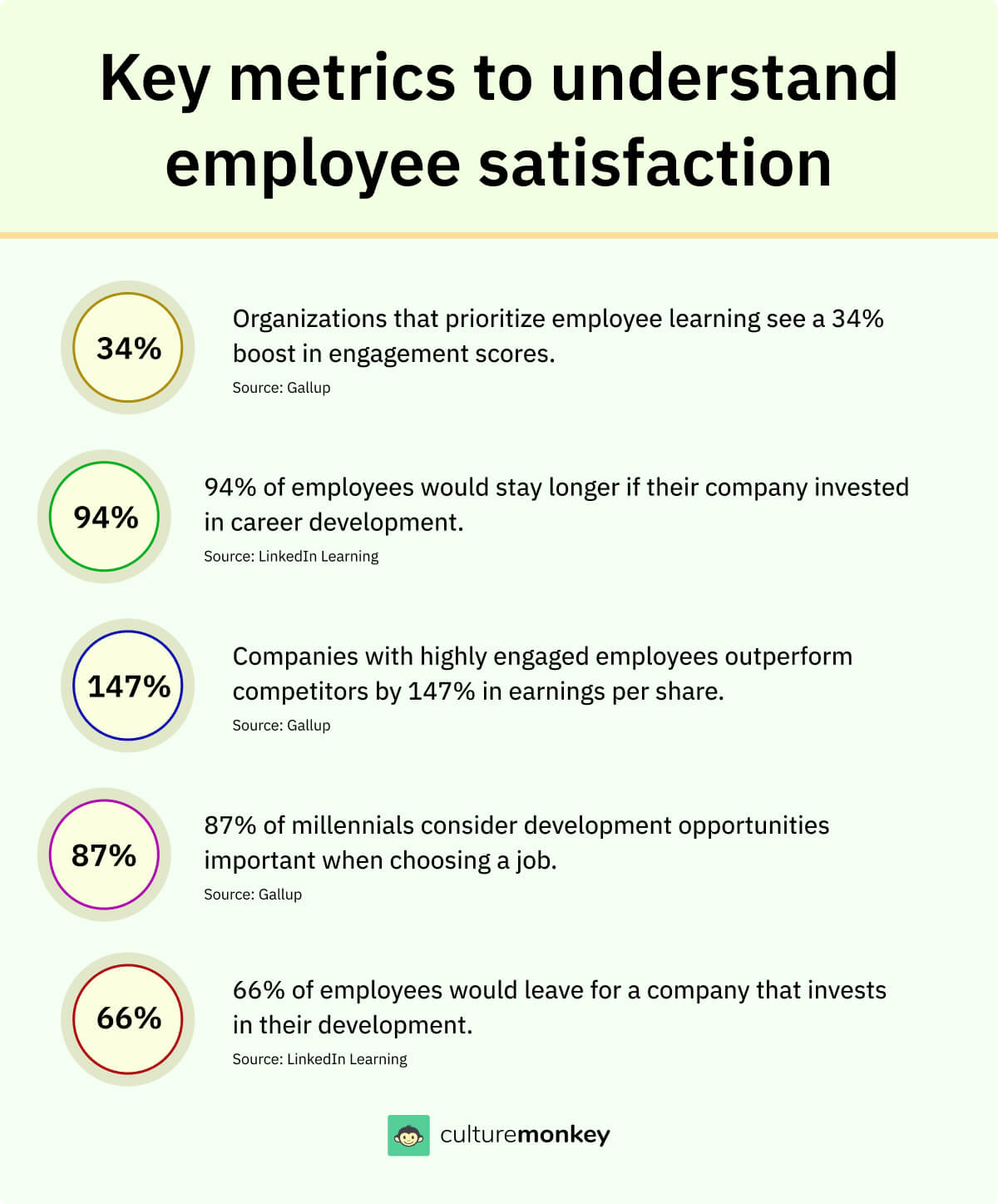
What is the engagement score?

The engagement score is a quantitative measure that represents the level of employee engagement within an organization. It is a numerical value derived from the analysis of employee engagement survey data or other relevant metrics.
The specific calculation of an engagement score may vary depending on the methodology used by the organization or the survey instrument employed.
Typically, it involves aggregating responses to survey questions that assess different dimensions of engagement, such as job satisfaction, organizational commitment, sense of belonging, and motivation.
These responses are often scored on a Likert scale, with higher scores indicating higher levels of engagement.
The staff engagement score provides organizations with a quantitative measure to track and monitor employee engagement trends. It offers a snapshot of the current state of engagement and can help identify areas of strength and areas for improvement.
It's important to note that the engagement score is just one piece of the puzzle when it comes to understanding employee engagement index. Qualitative feedback, open-ended survey responses, and other contextual factors should also be considered to gain a comprehensive understanding of the underlying drivers of engagement.
What is the best way to measure engagement?

Measuring employee engagement is crucial for organizations to understand the level of employee satisfaction score, commitment, and motivation.
Here are some best practices for measuring engagement:
- Employee engagement surveys: Use carefully designed surveys to assess areas like job satisfaction, communication, and work-life balance. Administer electronically or on paper, ensuring anonymity for honest feedback.
- Pulse surveys: Conduct shorter, focused surveys monthly or quarterly to gather real-time feedback. Use them to track changes in engagement, monitor specific initiatives, and identify emerging trends.
- Focus groups and interviews: Facilitate group discussions or one-on-one interviews to gather detailed, qualitative insights. These sessions allow employees to share concerns, suggestions, and ideas for improvement.
- Observation and feedback from managers: Managers can observe team behaviors, attitudes, and enthusiasm during daily interactions. Their feedback offers valuable qualitative insights into engagement levels and team dynamics.
- Performance metrics and business indicators: Analyze metrics like productivity, absenteeism, turnover, and customer satisfaction to uncover correlations with engagement. These indicators provide indirect yet actionable insights.
What metrics measure engagement?

Measuring employee engagement requires the use of various metrics that provide insights into different aspects of engagement within an organization. Here are some common metrics used to measure employee engagement:
- Response rates: Tracks the percentage of employees participating in surveys. High response rates indicate interest and engagement. Ensures data is reliable and representative.
- Retention rates: Measures the percentage of employees staying with the organization. High retention reflects effective engagement and a positive workplace experience.
- Absenteeism and sick leave: Monitors employee absence frequency and duration. Lower absenteeism suggests higher engagement, while spikes may indicate stress or dissatisfaction.
- Performance metrics: Tracks productivity, quality, and goal achievement. Engaged employees typically perform better, linking engagement to business outcomes.
- Employee net promoter score (eNPS): eNPS Measures how likely employees are to recommend the organization. Higher scores indicate stronger engagement and satisfaction.
- Employee feedback and suggestions: Gathers qualitative insights through feedback channels. Helps uncover engagement drivers and improvement areas.
- Peer recognition and awards: Tracks recognition frequency among employees. Higher recognition indicates engagement and a supportive workplace culture.

Ask the right questions,
get better results
Discover 20 essential questions to measure, understand, and enhance your employee engagement score.
How to calculate engagement score?

Calculating an engagement score involves aggregating and analyzing data from employee engagement surveys or other relevant metrics. While the specific calculation method may vary depending on the organization's approach, here is a general framework for calculating an engagement score:
- Determine engagement factors: Start by identifying the key factors that contribute to employee engagement within your organization. These factors may include job satisfaction, organizational commitment, communication effectiveness, growth opportunities, and work-life balance.
- Design survey questions: Develop a set of survey questions that assess each engagement factor. Use a Likert scale or a similar rating system to capture employees' responses to each question. Ensure that the questions are clear and concise, and cover the intended engagement factors.
- Administer the survey: Distribute the engagement survey to all employees within the organization. It can be conducted electronically, through an online survey platform, or on paper. Ensure that the survey is anonymous and that employees feel comfortable providing honest feedback.
- Score the survey responses: Assign numerical values to the responses based on the chosen rating scale. For example, if using a Likert scale ranging from 1 to 5, assign a value of 1 for "Strongly Disagree" and 5 for "Strongly Agree."
- Weight the engagement factors: If certain engagement factors are considered more important than others, assign appropriate weights to reflect their relative significance. Multiply the average score of each engagement factor by its corresponding weight to give it more or less influence on the overall engagement score.
- Calculate the engagement score: To calculate the overall engagement score, sum up the weighted or unweighted average scores of all engagement factors. This provides a single numerical value representing the level of employee engagement within the organization. The score can be presented as a percentage, a rating on a scale (e.g., 1 to 10), or any other format that suits your organization's needs.
- Analyze and interpret the results: Once the engagement score is calculated, analyze the results to identify areas of strength and areas for improvement. Compare the scores across different engagement factors and demographic groups to gain insights into variations in engagement levels. Use the findings to develop action plans and strategies that address specific engagement challenges and capitalize on areas of strength.
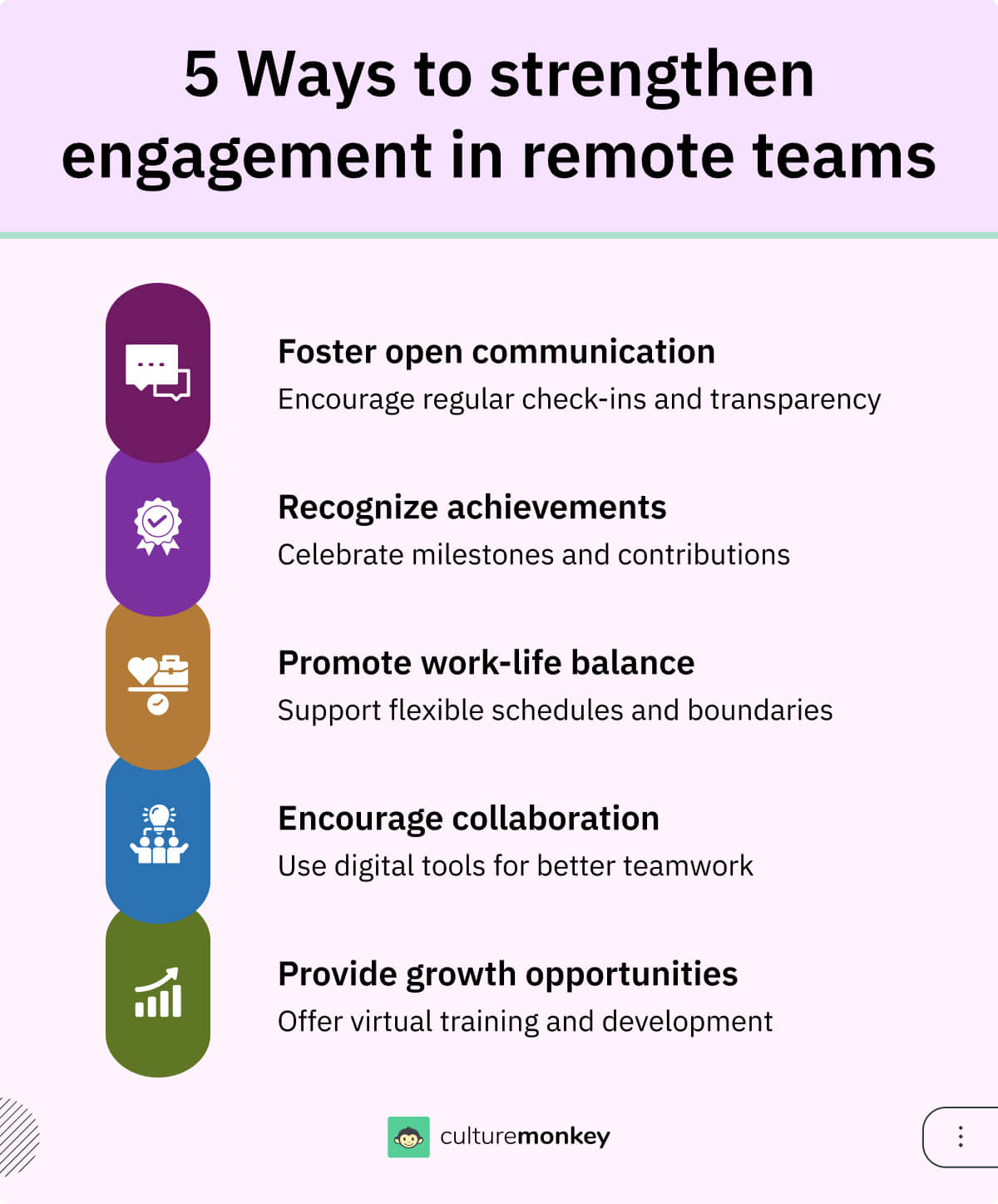
How to improve employee engagement score?
Improving your employee engagement score requires a strategic, ongoing effort that focuses on fostering a positive and engaging work environment. Here are unique strategies to elevate engagement effectively:
- Encourage cross-departmental collaboration: Break down silos by promoting cross-departmental collaboration. Organize projects or brainstorming sessions that require input from multiple teams to foster teamwork, innovation, and a sense of shared purpose.
- Empower employees with autonomy: Grant employees more autonomy in decision-making and daily tasks. Providing opportunities for ownership increases accountability, satisfaction, and overall engagement. Trusting employees to take the lead boosts morale and confidence.
- Personalized career development plans: Go beyond generic training programs by offering personalized career development plans tailored to individual employee goals. This shows a genuine interest in their growth, strengthening engagement and loyalty.
- Offer non-monetary rewards: Recognition doesn’t always have to involve monetary incentives. Celebrate achievements with personalized rewards, such as extra time off, mentorship opportunities, or access to special projects, to keep employees motivated.
- Enhance workplace design: A well-designed workspace improves tools to measure employee satisfaction measurement tools and engagement. Consider adding collaborative zones, quiet areas for focused work, or wellness spaces that contribute to a positive work environment.
- Promote community involvement: Encourage employees to participate in community service or charity work supported by the organization. Connecting employees with meaningful causes fosters a deeper sense of purpose and engagement.
Employee engagement score examples

- 1 to 5 scale: On a scale where 1 represents low engagement and 5 represents high engagement, a score above 4 typically indicates a highly engaged workforce.
- Percentage-based scoring: In systems where engagement is scored as a percentage, a score above 80% is generally considered a sign of strong employee engagement.
- eNPS (Employee Net Promoter Score): For eNPS, which ranges from -100 to +100, a score of +50 or higher is often seen as excellent, reflecting high levels of engagement and satisfaction.
- Context-specific scoring: A manufacturing company may consider a score of 75% highly engaged, while a tech company with higher industry benchmarks might target 85% or more.
- Departmental or team scores: Scores above 4.5 on a 1 to 5 scale in key teams or departments often suggest high engagement in those specific groups.
- Pulse survey scores: Monthly pulse survey metrics showing consistent scores above 8 out of 10 signal positive trends in employee engagement over time.
What is a good employee engagement score?

While there is no universal standard or fixed threshold for a "good" score, there are some general considerations to help interpret and evaluate engagement scores:
- Internal comparison: An effective way to assess the level of engagement scale score is by comparing it to previous scores within the organization. Tracking engagement trends over time allows organizations to gauge progress and improvement.
- External comparison: Benchmarking against industry standards or similar organizations can provide valuable insights. Industry-specific surveys or reports may provide average engagement scores, allowing for a comparison to determine how the organization fares about its peers.
- Contextual factors: Employee engagement is influenced by various factors such as organizational culture, work environment, and employee demographics. Consider the specific circumstances and challenges within the organization when evaluating the engagement score. For instance, if the organization recently underwent significant changes or faced operational challenges, the engagement score may be lower temporarily.
- Qualitative feedback: Analyzing open-ended survey responses, conducting focus groups, or gathering feedback through other channels can offer deeper insights into the underlying factors driving engagement or areas for improvement.
- Employee perception: Assess how employees perceive the work environment, their level of job satisfaction metrics, and their overall commitment to the organization. Consider conducting additional surveys or feedback mechanisms to capture employee sentiment and validate the engagement score.
Which employee satisfaction measurement channels should you use?
Measuring employee satisfaction metrics is crucial to understanding their needs, identifying pain points, and fostering a positive work environment. To ensure comprehensive insights, organizations can leverage a variety of measurement channels. Below are some unique options:
- 360-degree feedback programs: This method collects feedback from multiple sources, including peers, managers, and direct reports, providing a holistic view of employee satisfaction score. It helps uncover hidden issues, build trust, and promote transparency.
- Employee journey mapping: Analyze satisfaction at different stages of the employee lifecycle, such as onboarding, career progression, and exit. This channel identifies key moments that shape satisfaction and engagement, allowing organizations to address gaps proactively.
- Sentiment analysis tools: Use AI-driven tools to analyze employee comments in emails, chat platforms, or feedback forums. These tools help gauge overall sentiment and uncover recurring themes, offering real-time insights without waiting for formal surveys.
- Town hall meetings: Host interactive town hall meetings to directly address employee concerns and gather live feedback. This fosters open communication and gives employees a platform to voice their opinions in real-time.
- Wellness program feedback: Monitor participation and feedback from wellness initiatives, such as mental health programs or fitness activities. High participation and positive feedback often indicate improved satisfaction and well-being.
- Stay interviews: Conduct one-on-one stay interviews with high-performing employees to understand what keeps them satisfied and committed. This proactive approach helps uncover insights before employees consider leaving.
What are the indicators of a bad employee engagement score?

While specific indicators may vary, here are some common signs that suggest a poor employee engagement score:
- High turnover rates: When employees are disengaged, they are more likely to seek opportunities elsewhere, leading to increased turnover. High turnover rates can disrupt productivity, increase recruitment and training costs, and impact team morale.
- Low productivity: Disengaged employees may exhibit reduced motivation, lack of focus, or decreased effort in their work, resulting in lower overall productivity levels. Consistently low productivity can have negative effects on business outcomes and hinder organizational growth.
- Increased absenteeism and sick leave: Higher rates of absenteeism can indicate disengagement and lack of commitment to work. Excessive absenteeism can impact overall organizational performance.
- Lack of initiative and innovation: Disengaged employees may be less likely to contribute new ideas, offer suggestions for improvement, or take on additional responsibilities.
- Decreased customer satisfaction: Disengaged employees may provide subpar customer service or fail to meet customer expectations, leading to decreased customer satisfaction. Unsatisfied customers can have a detrimental impact on the organization's reputation, customer retention, and bottom line.
- Poor communication and collaboration: A lack of effective communication and collaboration among employees can indicate low engagement. This can hinder information flow, decision-making processes, and overall organizational effectiveness.
- Low employee morale and negative workplace atmosphere: Disengaged employees often experience lower morale, leading to a negative workplace atmosphere. A negative workplace environment can further contribute to disengagement and hinder employee well-being.

What to do after measuring employee engagement?

After measuring employee engagement, organizations should take appropriate steps to leverage the insights gained from the measurement process. Here are some actions to consider when assessing employee engagement:
- Analyze the data: Thoroughly analyze the data collected from the employee engagement measurement. Look for patterns, trends, and areas of strength or concern. Identify specific engagement factors that require attention or improvement.
- Share the results: Communicate the findings of the engagement measurement with relevant stakeholders, including leadership, managers, and employees. Transparently sharing the results helps create awareness and demonstrates the organization's commitment to addressing engagement issues.
- Identify root causes: Dig deeper into the data to identify the underlying factors influencing engagement levels. Look for connections between engagement scores and other organizational variables, such as communication, leadership, workload, or career development. Understanding the root causes will guide targeted interventions.
- Develop action plans: Based on the analysis and identified root causes, develop action plans to address the areas that need improvement. Establish clear goals, strategies, and initiatives to enhance employee engagement. Assign responsibilities and set timelines for implementation.
- Involve employees: Employee engagement is a shared responsibility. Involve employees in the process by seeking their input, ideas, and feedback on potential solutions. This promotes ownership, encourages buy-in, and increases the likelihood of successful implementation.
- Provide training and development: Invest in training and development programs that empower employees and enhance their skills, knowledge, and abilities. Offer opportunities for career growth, professional development, and continuous learning. This demonstrates the organization's commitment to employee growth and fosters a sense of engagement.
- Enhance communication: Strengthen communication channels within the organization to improve transparency, clarity, and employee involvement. Foster open dialogue, actively listen to employee feedback, and address concerns promptly. Effective communication builds trust and engagement.
- Recognize and reward: Implement recognition and reward programs to acknowledge and appreciate employees' contributions and achievements. Celebrate successes and milestones, both individual and team-based. Recognition and rewards boost morale and reinforce a culture of appreciation.
- Monitor progress: Continuously monitor and measure engagement levels over time to track progress. Regularly assess the impact of implemented initiatives and interventions. Use feedback mechanisms, pulse surveys, or follow-up engagement measurements to gauge improvements and make adjustments as needed.
- Foster a positive work environment: Create a positive work environment that promotes work-life balance, inclusivity, and well-being. Support employee wellness initiatives, provide flexible work options when feasible, and foster a culture of trust, respect, and collaboration.
Conclusion
Understanding and effectively utilizing your employee engagement score is essential for fostering a motivated, satisfied, and high-performing workforce. While engagement scoring systems may vary across organizations, the goal remains the same—to identify strengths, address weaknesses, and create a workplace where employees feel valued and committed.
CultureMonkey makes this process seamless by offering robust tools to measure, analyze, and improve employee engagement. With its intuitive interface and data-driven insights, CultureMonkey empowers organizations to take meaningful action based on engagement scores.
In today’s competitive landscape, having a reliable employee engagement platform like CultureMonkey isn’t just an option—it’s a necessity for building a thriving organization.
Summary
Strengths in the workplace are crucial for boosting employee engagement and productivity. Identifying and leveraging strengths helps employees excel in their roles and contributes to organizational success. Recognizing strengths leads to higher job satisfaction, better team dynamics, and improved performance. Managers can foster a strengths-based culture by using tools like surveys, offering feedback, and tailoring development opportunities to individual talents.
FAQs
1. What is the employee satisfaction index?
The Employee Satisfaction Index (ESI) is a metric that quantifies how satisfied employees are with their work, leadership, and overall workplace experience. It provides a clear picture of employee sentiment, helping organizations track satisfaction trends and identify areas for improvement. A high ESI indicates a motivated workforce, while a low ESI highlights dissatisfaction, making it a valuable tool for enhancing workplace culture and retention.
2. How to calculate the employee satisfaction index?
To calculate the Employee Satisfaction Index (ESI), ask employees to rate satisfaction on a scale (e.g., 1 to 10). Average the responses, divide by the maximum score, and multiply by 100 to get a percentage. For example, an average score of 7.5/10 would result in a 75% satisfaction index, signaling moderately high satisfaction. This standardized method ensures consistent, actionable insights.
3. Why should you measure employee engagement?
Measuring employee engagement allows organizations to understand how motivated, satisfied, and committed their workforce is. Engaged employees are more productive, loyal, and aligned with company goals. Engagement data highlights organizational strengths and areas needing improvement, empowering leaders to create strategies that enhance culture, communication, and performance, ultimately driving business success and employee well-being.
4. How often should employee engagement be measured?
Employee engagement should be measured annually for a comprehensive view, with additional pulse surveys conducted quarterly or monthly for timely insights. Regular measurement helps organizations stay aligned with evolving employee needs, identify and address issues early, and track the effectiveness of engagement initiatives over time, ensuring continuous improvement in workplace culture.
5. How should organizations act on employee engagement survey results?
Organizations should carefully analyze survey data to uncover trends and problem areas. Prioritize actionable insights, develop targeted strategies, and assign clear ownership for execution. Communicate the results and planned actions to employees transparently, involve them in the process, and follow up with regular progress updates. Acting on feedback fosters trust, boosts morale, and drives meaningful engagement improvements.
6. Can engagement scores vary across teams or departments?
Engagement score meaning often vary between teams or departments due to factors like leadership style, workload, or team dynamics. For example, a department with supportive leadership may show higher engagement than one struggling with communication issues. Understanding these variations enables organizations to create tailored solutions that address specific challenges, ensuring that engagement improves across all levels of the business.




