What is employee offboarding: Best practices and checklist to follow in 2025

Remember the last day of summer vacation as a kid? The sun was setting, the ice cream truck’s jingle was fading, and that sinking feeling hit—you had to go back to school tomorrow. Your freedom? Over. Your lazy afternoons? Gone. Even your favorite cereal didn’t taste the same that morning. That was the bittersweet art of endings—something we rarely talk about but feel deeply.
Now, fast forward to the workplace. Employees come and go, but how they leave can make or break your company’s morale. Offboarding isn’t just an HR formality—it’s your last chance to create a lasting impression, protect your culture, and ensure a smooth transition.
In 2025, when employee experience defines brand reputation, how you handle exits will say just as much about you as how you welcome new hires. So, how do you keep morale high amidst departures? Let’s dive in.
Employee offboarding definition

Beyond logistics, a thoughtful employee offboarding process protects employer branding and team morale. When done right, offboarding demonstrates respect and clarity, reassuring current employees and strengthening trust in leadership. According to the offboarding definition, it’s not just about exits—it’s about transitions done with dignity.
A well-designed offboarding policy can even transform departing staff into brand advocates. Employees who leave on good terms may refer top talent, open doors to business opportunities, or return as rehires.
With digital tools and offboarding surveys, companies can gather honest feedback to improve culture and retention. Automating the employee offboarding process ensures consistency while maintaining compliance and data security.
So, what does offboarding mean today? It means using structured workflows, insights, and empathy to craft offboarding experiences that are as meaningful as onboarding—because offboarding meaning in HR goes far beyond a goodbye.
Why is offboarding important to HR leaders?

Offboarding plays a crucial role in the employee lifecycle, helping HR leaders maintain organizational effectiveness, safeguard company culture, and strengthen employer branding. Here’s why it’s a key priority:
- Protecting organizational reputation: Managing departures professionally ensures a positive employer brand. Respectful employee offboarding reduces negative perceptions among employees, clients, and stakeholders.
- Preserving knowledge and continuity: A structured employee offboarding process facilitates knowledge transfer. HR leaders ensure critical skills and expertise are retained within the organization.
- Mitigating legal and compliance risks: Adhering to legal regulations and documenting exits properly prevents disputes. HR teams safeguard the organization from potential litigation and compliance breaches.
- Managing talent pipelines: Insights from offboarding surveys reveal turnover trends and skills gaps. Analyzing exit data helps HR leaders refine succession planning and recruitment strategies.
- Enhancing employee experience: A well-managed exit fosters goodwill and positive relationships. Employees who experience the best employee offboarding experiences may return as boomerang hires or refer top talent.
What are the objectives of offboarding?
A well-structured employee offboarding process ensures a smooth transition while benefiting both the departing employee and the organization. Beyond just formalities, offboarding serves several critical objectives that contribute to long-term success.
- Ensuring a seamless transition: Offboarding helps in the structured transfer of responsibilities, ensuring minimal disruption to workflows. This process maintains business continuity and prevents knowledge gaps.
- Protecting company security: Revoking access to company systems, retrieving assets, and securing confidential information are essential aspects of offboarding. These steps mitigate risks and uphold cybersecurity measures.
- Gathering valuable feedback: Conducting offboarding surveys and exit interviews provides insights into employee experiences. This feedback helps identify areas of improvement and enhances workplace culture.
- Maintaining positive relationships: Strong alumni networks and post-departure engagement contribute to the best employee offboarding experiences. Keeping former employees engaged can lead to referrals or future collaborations.
- Strengthening employer branding: A thoughtful offboarding definition leaves a lasting impression, reinforcing the company’s reputation. Employees who depart on good terms become brand ambassadors.
- Supporting employee well-being: Offering career guidance, severance benefits, or outplacement services reflects an empathetic work culture. A supportive approach ensures a smooth transition for employees.
- Driving organizational improvements: Analyzing exit data helps HR refine policies and retention strategies. Understanding what are the objectives of offboarding fosters continuous workplace enhancement.
- Ensuring compliance and legal clarity: A structured employee offboarding process ensures all exit formalities of an employee are completed in line with labor laws and internal policies. This reduces legal risks and keeps the company audit-ready.
- Enabling smoother workforce planning: Timely offboarding provides visibility into resource gaps, allowing HR and leadership to proactively manage backfills or restructuring—streamlining the employee offboarding HR workflow.
- Reinforcing company values and culture: Executing offboarding with professionalism and empathy reflects your internal culture and values, giving meaning to what does offboarding mean beyond just operational tasks.
Benefits of effective employee offboarding
A well-executed employee offboarding process does more than close a chapter—it opens the door to organizational growth, talent advocacy, and risk reduction. Here’s how:
- Protects company data and security: Timely deactivation of accounts, retrieval of assets, and revocation of access prevent potential breaches—an essential part of any strong offboarding policy.
- Preserves institutional knowledge: When handled properly, offboarding includes structured knowledge transfer that supports continuity and prepares the next employee for success.
- Enhances employer branding: Positive offboarding experiences turn former employees into advocates, boosting referrals and reputation—especially when offboarding meaning in HR is tied to respect and transparency.
- Reduces legal and compliance risks: A defined offboarding definition ensures proper documentation, severance, and compliance with labor laws, protecting the organization from liabilities.
- Provides actionable insights: Exit interviews and feedback help refine internal policies and understand what does offboarding mean from the employee’s perspective, contributing to retention improvements.
- Strengthens employee morale: When remaining employees see that offboarding employees are treated with fairness, it reinforces trust in leadership and fosters a healthy culture.
Onboarding and offboarding: What's the difference?
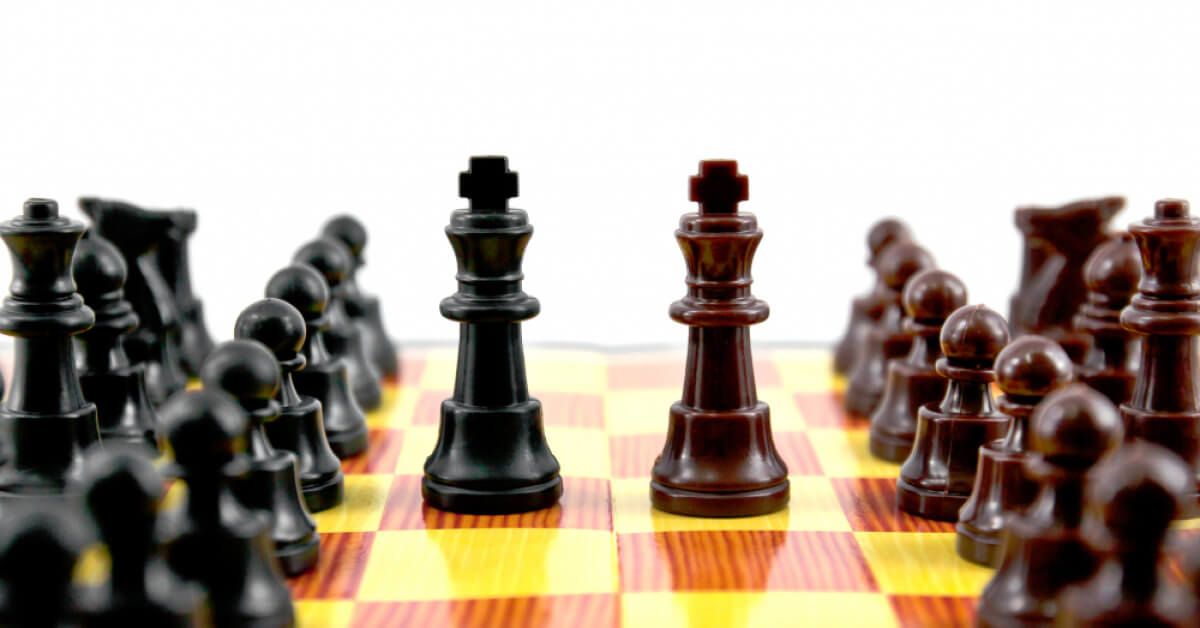

| Aspect | Onboarding | Offboarding |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A structured process designed to welcome and integrate new employees into the organization. | The process of managing an employee’s departure from the organization. |
| Timing | Begins when a candidate accepts a job offer and extends through their initial weeks or months. | Starts when an employee resigns, retires, or is terminated. |
| Objective | Helps new hires acclimate to company culture, policies, and expectations for long-term success. | Ensures a smooth exit while preserving knowledge, relationships, and company reputation. |
| Key activities | Orientation sessions, training programs, introductions to colleagues, and providing necessary resources. | Exit interviews, returning company property, transferring responsibilities, and handling legal and administrative tasks. |
| Impact on employee experience | Creates a positive first impression, boosts engagement, and enhances retention. | Shapes the final impression, influences alumni relations, and protects employer branding. |
| Value to organization | Ensures employees quickly become productive and aligned with company goals. | Minimizes operational disruptions and offers insights for improving workplace culture. |
What is an employee offboarding process?

A structured employee offboarding process ensures a respectful and seamless departure while maintaining business continuity. Here are the essential steps:
- Administrative closure: Finalize paperwork, manage exit formalities of an employee, and ensure legal compliance—key elements of the employee offboarding HR workflow and part of every solid offboarding policy.
- Asset retrieval: Collect company property such as laptops and ID cards to protect sensitive information—an essential part of the HR offboarding process and aligned with offboarding best practices.
- Knowledge transfer: Document important tasks and train successors, making the onboarding and offboarding meaning equally critical for business continuity.
- Emotional support: Address the personal side of transitions with empathy and open communication—this reinforces employee offboarding meaning and showcases best practices for employee offboarding.
- Exit interviews: Use feedback from departing employees to improve internal practices, supporting the offboarding process meaning and fulfilling what is the objective of offboarding.
- Responsibility transition planning: Plan the handover of duties and client responsibilities as part of a strategic and secure off-boarding meaning initiative.
- Feedback loop implementation: Conduct offboarding surveys to continuously improve your offboarding approach and enhance future processes by understanding what is offboarding and what does offboarding mean from both organizational and human perspectives.
Types of offboarding that you should know

A well-structured employee offboarding process ensures smooth transitions while maintaining compliance and positive relationships. Here are the key types of staff offboarding:
- Voluntary offboarding – Occurs when an employee chooses to leave due to career opportunities, personal reasons, or retirement. This allows organizations to gather insights through exit interviews, reinforcing offboarding best practices.
- Involuntary offboarding – Happens when an organization terminates employment due to performance, restructuring, or economic reasons. It requires compliance with legal standards and ethical handling to align with what is the purpose of offboarding.
- Retirement offboarding – Ensures a seamless transition when employees retire, including retirement planning, farewell celebrations, and knowledge transfer, demonstrating what is offboarding beyond just an exit.
- Redundancy offboarding – Takes place when a role becomes redundant due to mergers or automation. Providing career support and retraining helps employees navigate what are the typical offboarding tasks.
- Contract offboarding – Marks the end of a fixed-term employment contract, requiring clear communication, notice periods, and transition planning to align with onboarding and offboarding meaning.
Offboarding and boomerang employees
A well-executed employee offboarding process doesn’t just facilitate smooth exits—it also lays the groundwork for potential returns. Boomerang employees, or those who leave and later rejoin, bring valuable experience and familiarity, making them a strategic asset for organizations.
- Creating a positive exit experience: A respectful, well-structured offboarding definition ensures departing employees feel valued. When employees leave on good terms, they are more likely to consider returning in the future.
- Maintaining alumni engagement: Establishing alumni networks, newsletters, and check-ins helps companies stay connected with former employees. Strong post-exit relationships contribute to the best employee offboarding experiences and potential rehiring opportunities.
- Leveraging offboarding surveys for insights: Conducting offboarding surveys allows organizations to understand why employees leave. These insights help improve retention strategies and create an environment that welcomes returning talent.
- Positioning rehiring as an opportunity: Communicating that the company values and welcomes returning employees reinforces an open-door policy. Having a structured employee offboarding process encourages former employees to view the organization as a future career option.
- Enhancing organizational knowledge transfer: When boomerang employees return, they bring external industry insights along with prior company knowledge. Their seamless reintegration boosts productivity and innovation while strengthening company culture.
Employee offboarding checklist to follow in 2025

As we step into 2025, mastering the art of employee offboarding is more critical than ever. A well-thought-out checklist ensures a seamless transition for departing employees and leaves a positive impact on both the team and the organizational culture.
Pre-offboarding preparation
- Inform relevant stakeholders: Notify the necessary departments about the impending departure to facilitate a smooth transition.
- Plan knowledge transfer sessions: Schedule sessions for departing employees to share crucial insights and documentation with their team.
- Set up exit interviews: Prepare for exit interviews to gather valuable feedback that can guide future organizational improvements.
Last days logistics
- Return company property: Ensure that departing employees return any company-owned equipment, access cards, or any other company property or assets.
- Provide access details: Grant access to collaborative tools and systems required for ongoing collaboration, making the transition smoother.
- Discuss final responsibilities: Clearly outline any remaining tasks or responsibilities to be completed before the departure.
Post-departure engagement
- Keep the door open: Encourage departing employees to maintain professional connections, fostering potential collaborations or partnerships.
- Conduct follow-up survey: After a few months, conduct a follow-up survey to gain insights into the post-departure experiences of former employees.
- Share positive stories: Highlight positive stories about the departing employee, contributing to a positive corporate culture.
Documentation and compliance
- Complete paperwork: Ensure all necessary paperwork, including exit forms and non-disclosure agreements, is completed.
- Secure company data: Safeguard sensitive company data by revoking access and recovering any remaining company property.
- Legal compliance: Ensure compliance with legal requirements related to the employee's departure, protecting both the employee and the organization.
Post-departure support
- Provide career transition resources: Offer departing employees access to career counseling services or professional development opportunities to support their transition to new employment.
- Extend benefits information: Inform departing employees about their post-employment benefits, such as COBRA coverage for health insurance or retirement plan options, ensuring they understand their entitlements and deadlines for enrollment.
- Offer alumni network membership: Invite departing employees to join the company's alumni network, providing them with ongoing networking opportunities, fostering a sense of connection and support even after they've left the organization.
Continuous improvement
- Analyze offboarding data: Review offboarding data and feedback to identify trends, areas for improvement, and opportunities to enhance the offboarding process.
- Update offboarding checklist: Continuously updatethe offboarding checklist based on feedback and changing organizational needs, ensuring it remains relevant and effective.
- Conduct offboarding process audits: Regularly audit the offboarding process to ensure compliance with legal requirements, alignment with organizational policies, and adherence to industry standards.
What is the employee exit process?
Following the checklist given above, you can orchestrate the departure of your employee with finesse. It's not just bidding adieu; it's a well-choreographed routine encompassing several key steps.
- A structured farewell: The employee exit process involves formalities that go beyond the surface. It starts with a heads-up to relevant stakeholders, setting the stage for a smooth departure. This isn't just about an employee leaving; it's a strategic act that considers the broader impact a leaving employee has on the team and the organization.
- Notification and coordination: Informing the right parties promptly is the opening move. Whether it's the HR team, immediate colleagues, or project partners, effective communication sets the tone. Think of it as sending out invitations to a performance where everyone needs to be on the same page.
- Preparing for knowledge transfer: A standout feature of the exit process is knowledge transfer. It's not just about saying goodbye; it's about sharing insights, processes, and expertise. Think of it as passing the baton in a relay race, ensuring the momentum continues even after the departure.
- The final act: Exit interviews: Exit interviews are the grand finale. They're not just a formality; they're an opportunity to capture valuable feedback. Like a post-show critique, exit interviews provide insights into the employee's journey, offering a script for improving future performances.
- Transitioning smoothly: The exit process isn't about closing a chapter abruptly; it's about transitioning smoothly. From returning company property to wrapping up final responsibilities, each step is a carefully choreographed move to maintain the rhythm of business operations.
- Conclusion: The employee exit process is a well-structured performance that transcends mere goodbyes. It's a strategic play that, when done right, sets the stage for future employees' successes. As the curtain falls on one employee's journey, the spotlight shifts to a well-prepared stage for the next act in the company's narrative.
17 Employee offboarding best practices to follow in 2025

Employee offboarding should go beyond traditional norms to be considered great. Embrace these cutting-edge best practices to ensure a seamless and positive departure experience for both departing employees and the entire organization:
- Open transparent channels early: Initiate the offboarding process before the last day. Early communication fosters transparency, reducing uncertainty and setting the stage for a collaborative departure.
- Leverage technology for exit interviews: Embrace technology for exit interviews. Virtual or AI-assisted interviews can offer a comfortable space for honest feedback, providing valuable insights for organizational improvement.
- Develop a boomerang employee program: Establish a boomerang employee program, encouraging departing employees to consider returning in the future. This not only maintains a positive connection but also taps into known talents when needed.
- Prioritize cybersecurity: Prioritize cybersecurity in the offboarding process. Revoke access promptly, safeguarding against potential security breaches and protecting sensitive company data.
- Personalized farewell experience: Craft a personalized farewell experience. Tailor the offboarding process to individual preferences, reflecting a company culture that values the unique contributions of each team member.
- Implement post-departure surveys: Extend feedback opportunities beyond exit interviews. Implement post-departure surveys a few months after an employee leaves to gain insights into their experiences and identify areas for improvement.
- Facilitate alumni networking: Create opportunities for departed employees to stay connected. Alumni networking events or online platforms foster ongoing relationships, potentially leading to collaborations or partnerships.
- Showcase positive departure stories: Share positive departure stories as part of your employer branding. Highlighting successful offboarding experiences reinforces positive company culture and attracts top talent in the long run.
- Continuous improvement through data analysis: Utilize data analytics from exit interviews and surveys for continuous improvement. Analyzing trends and patterns provides a strategic roadmap for enhancing the overall employee experience.
- Encourage knowledge transfer sessions: Introduce knowledge transfer sessions as a part of the offboarding process. Encourage departing employees to share their expertise with their colleagues, ensuring a smooth transition and preserving institutional knowledge within the organization.
- Offer flexible departure options: Provide departing employees with flexible departure options, such as phased exits or remote work arrangements during their notice period, accommodating individual circumstances and preferences while ensuring a smooth transition for the team.
- Arrange farewell celebrations: Organize farewell celebrations or gatherings to honor departing employees and recognize their contributions to the organization. These events can include farewell lunches, happy hours, or team outings, providing an opportunity for colleagues to express their appreciation and bid farewell in a positive and memorable way.
- Provide career transition support: Offer resume-building assistance, job referrals, or career coaching. Supporting employees post-exit builds goodwill and maintains positive alumni relations.
- Ensure emotional well-being check-ins: Assign a mentor or HR contact for emotional support. Addressing the psychological impact of offboarding fosters a caring company culture.
- Document best practices from top performers: Create an offboarding knowledge repository. This ensures that valuable expertise is retained and can be leveraged for future success.
- Send personalized thank-you messages: A handwritten note or personalized email from leadership can leave a lasting impression. A simple gesture of gratitude reinforces positive employer-employee relationships.
- Extend employee discounts and perks post-exit: Offer limited-time access to company discounts or alumni benefits. Small perks help maintain goodwill and engagement even after departure.
How to be more empathetic with employee offboarding?

In 2025, we're all about making farewells feel more like 'see you later.' Here's your friendly guide on infusing a touch of approachability into your offboarding process:
- Start the conversation early and openly: Let your team in on the news sooner rather than later. Opening up about departures in a timely and transparent way helps everyone get on the same page and fosters a sense of shared understanding.
- Craft tailored support plans: Recognize that everyone's journey is different. Tailor your support plans to each individual, acknowledging their unique needs and concerns. It's like offering a departure plan made just for them.
- Regular check-ins beyond the formalities: Go beyond the usual 'How are you?' Include emotional check-ins throughout the offboarding process. Create a space for your departing team members to share feelings and concerns, showing that their well-being matters beyond the workplace.
- Flexible departure timelines when possible: Realize that transitions take time. Offer flexibility in departure timelines when you can. This shows you understand the emotional weight of saying goodbye and are willing to make it a bit easier.
- Access to counseling and resources: Extend a helping hand beyond work matters. Provide your employee access to counseling services and resources, showing that your support goes beyond the office walls to their overall well-being.
- Cheers for contributions and gratitude: Celebrate your departing team member's contributions. Take a moment to acknowledge their achievements and express gratitude for their time with the team. It's like a virtual high-five for a job well done.
- Encourage heartfelt conversations: Create a space for open dialogue. Encourage your departing team members to share thoughts and concerns, fostering trust and understanding. This way, they know their voice matters.
- Stay in the loop with the alumni network: Keep them in the loop with the company's alumni network. This friendly gesture ensures they're not just leaving but joining a community. Who knows what exciting collaborations might come from it?
- Exit interviews, your way: Make exit interviews as easy as a chat with a friend. Offer flexibility in the format - written, virtual, or one-on-one - whatever suits their style best.
- Keep the support going: Be there even after the last day. Implement a follow-up system to check on your former team members in the weeks and months following their departure. It's like a virtual wave, letting them know you're cheering them on in their next adventure.
10 Challenges during offboarding

The offboarding process, although often overshadowed by its counterpart, onboarding, plays a pivotal role in the employee lifecycle. It is a period of transition that demands careful attention to detail, sensitivity, and strategic planning. However, despite its importance, offboarding presents a unique set of challenges for organizations to overcome.
- Emotional impact: Offboarding can evoke a range of emotions for both departing employees and their colleagues. Challenges may arise from managing feelings of loss, resentment, or uncertainty among team members, affecting morale and productivity.
- Knowledge transfer: Ensuring a smooth transfer of knowledge from departing employees to their successors can be challenging. Difficulties may arise in capturing and documenting critical information, skills, and insights, leading to gaps in institutional knowledge and potential disruptions to business operations.
- Legal compliance: Navigating the complex legal landscape of offboarding presents challenges for organizations. Compliance with federal, state, and local laws regarding final pay, benefits continuation, non-disclosure agreements, and anti-discrimination measures requires careful attention to detail to avoid legal risks and potential liabilities.
- Confidentiality and data security: Safeguarding sensitive company information and protecting data security during offboarding presents significant challenges. Risks may arise from the mishandling or unauthorized disclosure of confidential information by departing employees, posing threats to intellectual property and regulatory compliance.
- Employee relations: Offboarding can strain relationships between departing employees and their colleagues or supervisors. Challenges may arise from managing interpersonal dynamics, addressing conflicts or grievances, and maintaining professionalism and respect throughout the offboarding process.
- Retention of institutional knowledge: Retaining institutional knowledge and expertise is crucial for organizational continuity. Challenges may arise from the loss of key personnel and their specialized skills or experiences, impacting operational efficiency, decision-making, and innovation.
- Transition management: Effectively managing the transition of responsibilities and workflows following an employee's departure presents challenges for organizations. Ensuring continuity of projects, client relationships, and daily operations while reallocating tasks and resources requires strategic planning and coordination.
- Reputation management: Offboarding incidents that are mishandled or perceived negatively can damage the organization's reputation. Challenges may arise from managing public perception, addressing media scrutiny, and mitigating reputational risks associated with high-profile departures or legal disputes.
- Employee morale and engagement: Offboarding can impact overall employee morale and engagement within the organization. Challenges may arise from addressing concerns, managing uncertainty, and maintaining a positive workplace culture amidst periods of transition and change.
- Retention and talent management: Offboarding challenges extend beyond the departing employee to include retention and talent management strategies. Organizations must navigate the potential impact on employee retention, succession planning, and recruitment efforts, ensuring a seamless transition for both departing and remaining staff.
Legal considerations during offboarding

As organizations strive to maintain compliance with legal standards while ensuring a smooth transition for departing employees, understanding the legal considerations in the offboarding process becomes paramount.
Severance agreements:
- Ensure that any severance agreements offered during offboarding comply with federal and state laws, including the requirements outlined in the Older Workers Benefit Protection Act (OWBPA) for employees aged 40 and older.
- Clearly outline the terms of severance, including payment amounts, timing, release of claims, confidentiality provisions, and any other relevant terms to protect the interests of both parties.
Final pay and benefits:
- Comply with state laws regarding the timing and method of final pay for departing employees, including payment of wages, accrued vacation time, bonuses, and any other outstanding compensation owed.
- Provide information to departing employees regarding their rights to continue health insurance coverage through COBRA (Consolidated Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act) or state continuation coverage, and ensure timely notification of their rights and obligations.
Return of company property:
- Require departing employees to return all company-owned property, including electronic devices, keys, access cards, uniforms, and any other materials issued by the organization.
- Clearly communicate the consequences of failing to return company property, including potential legal action or withholding of final paychecks, to ensure compliance and protect the organization's assets.
Non-Disclosure and Non-Compete agreements:
- Enforce non-disclosure and non-compete agreements as applicable, ensuring that departing employees understand their ongoing obligations regarding confidentiality, trade secrets, and competition with the organization.
- Review the enforceability of non-compete agreements based on state laws, as some jurisdictions have restrictions on the scope, duration, and enforceability of these agreements.
Protection of intellectual property:
- Take measures to safeguard intellectual property and trade secrets during offboarding, including revoking access to sensitive information, systems, and databases.
- Implement protocols for departing employees to certify that they have not retained or disseminated confidential information or proprietary materials belonging to the organization.
Documentation and record-keeping:
- Maintain accurate records of offboarding activities, including exit interviews, severance agreements, return of company property, and any communications related to the departure.
- Retain documentation in compliance with federal and state record-keeping requirements, ensuring accessibility and confidentiality of sensitive information.
Anti-discrimination and retaliation protections:
- Ensure that offboarding decisions are made in compliance with federal and state anti-discrimination laws, including Title VII of the Civil Rights Act, the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA), and the Age Discrimination in Employment Act (ADEA).
- Prohibit retaliation against departing employees who engage in protected activities, such as filing complaints of discrimination, harassment, or workplace safety concerns, and provide avenues for reporting and addressing such issues in a timely and effective manner.
Role of exit surveys in the offboarding process

Offboarding surveys go beyond a standard farewell—they serve as a crucial tool for organizational growth, talent retention, and continuous improvement. Here’s how they elevate the employee offboarding process:
- Gathering candid feedback: Exit surveys provide a platform for departing employees to share honest insights. This feedback helps organizations refine their employee offboarding checklist, ensuring an improved experience for future departures.
- Informing talent retention strategies: Understanding why employees leave enables companies to develop targeted retention efforts. Addressing concerns early enhances engagement and prevents avoidable turnover, contributing to the best employee offboarding experiences.
- Building trust and transparency: Conducting offboarding surveys signals that employee voices matter beyond their tenure. This strengthens trust, reinforcing an open culture aligned with the company’s offboarding meaning and values.
- Continuous improvement and policy adjustments: Feedback from exit surveys helps fine-tune HR policies. Aligning company policies with employee expectations ensures a seamless staff offboarding experience and long-term workforce satisfaction.
- Enhancing organizational culture: Insights from exit surveys highlight strengths and cultural gaps within the company. Strengthening cultural alignment ensures that offboarding definition extends beyond departures and contributes to lasting workplace improvements.
Using exit interview data analysis to improve employee retention
Exit interview data analyses serve as a compass, guiding organizations toward strategies that enhance employee retention rates without merely relying on conjecture.
- Understanding root causes: Exit interviews provide a rich dataset of employee experiences and sentiments. Through thorough analysis, organizations can pinpoint the root causes behind departures. This understanding goes beyond surface-level reasons, offering insights that enable targeted retention efforts.
- Identifying trends and patterns: Exit interview data analysis allows for the identification of trends and patterns. Recognizing recurring themes provides a strategic advantage in addressing systemic issues that may be contributing to a higher turnover rate. It's akin to deciphering a code that holds the key to employee satisfaction and loyalty.
- Tailoring retention strategies: Armed with insights from data analysis, organizations can tailor retention strategies to address specific pain points. This targeted approach ensures that interventions are not generic but crafted to resonate with the unique needs and expectations of the workforce.
- Proactive problem resolution: Exit interview data analysis enables proactive problem resolution. Instead of reacting to turnover after it occurs, organizations can preemptively tackle issues highlighted in the data, mitigating the risk of losing valuable talent and fostering an environment where employees feel heard and valued.
- Enhancing company culture: Understanding the sentiments expressed in exit interviews contributes to the enhancement of company culture. Data analysis helps in identifying aspects of the organizational culture that may need refinement.
- Strategic talent planning: Exit interview data serves as a valuable resource for strategic talent planning. By identifying patterns in employee departures, organizations can better plan for succession, ensuring continuity in critical roles and minimizing disruptions in business operations.
- Benchmarking against industry standards: Data analysis allows organizations to benchmark their retention efforts against industry standards. This external comparison provides context, helping organizations gauge the effectiveness of their strategies and make informed adjustments to stay competitive in talent retention.
Conclusion
From defining employee offboarding to uncovering the role of exit surveys and analyzing their data, we hope you benefit from these insights and best practices. A well-crafted and effective offboarding process, infused with empathy and backed by strategic data analysis, becomes a powerful tool for organizational growth.
As you move on the journey of refining your offboarding processes and enhancing your workplace culture, consider the tools and support available. CultureMonkey offers AI-driven employee offboarding surveys, real-time sentiment analysis, and actionable insights to help organizations turn exits into opportunities.
With automated employee offboarding checklist management, customizable feedback collection, and data-backed reports, CultureMonkey ensures the best employee offboarding experiences.
Let CultureMonkey be your partner in creating an offboarding strategy where goodbyes aren’t the end but a stepping stone to future success—one that strengthens employer branding, enhances retention, and fosters lasting connections.
FAQs
1. What happens during offboarding?
During offboarding, management ensures a smooth employee exit by collecting company assets, conducting exit interviews, and finalizing paperwork. The employee offboarding process may also include offboarding surveys and knowledge transfer. According to the offboarding definition, the process is designed to protect business continuity and reflect what being offboarded means in a professional setting.
2. What is the purpose of employee offboarding?
The purpose of employee offboarding is to manage exits respectfully and effectively. It includes finalizing documents, supporting transitions, and honoring contributions. A well-structured offboarding policy preserves knowledge and morale. Understanding what does offboarding mean—and how it fits into culture and compliance—ensures a seamless conclusion aligned with offboarding meaning in HR.
3. How can companies improve their offboarding procedures?
Companies can improve offboarding by using clear offboarding policies, training HR teams, and digitizing processes. Integrating offboarding surveys allows insights that refine the employee offboarding process. Defining what is offboarding as both logistical and emotional helps create consistency. These practices support efficient offboarding employees while promoting goodwill and future collaboration.
4. What role does HR play in the offboarding process?
HR leads the offboarding journey—from communication to compliance. Their role includes explaining procedures, managing documentation, and conducting offboarding surveys. As offboarding employees, HR ensures clarity and empathy. This reinforces what is off boarding, as HR defines the experience. Ultimately, HR’s role in offboarding shapes both process success and brand reputation.
5. What steps are involved in the offboarding process?
The offboarding process typically includes notifying stakeholders, conducting exit interviews, collecting assets, completing exit formalities of an employee, and handling legal paperwork. The employee offboarding HR workflow may also provide emotional support. These steps reflect the offboarding process meaning and align with best practices for employee offboarding, helping define the broader off-boarding meaning within organizational strategy.
6. How can companies maintain positive relationships with former employees after offboarding?
Companies can maintain relationships post-exit by fostering alumni networks, hosting events, and offering flexible opportunities. A thoughtful employee offboarding policy and consistent communication reinforce goodwill. This ensures best employee offboarding experiences, answering what is the objective of offboarding—to leave the door open for rehiring, referrals, and ongoing brand advocacy beyond formal employment.
7. Does offboarding include an exit interview?
Yes, the offboarding process typically includes an exit interview. According to the offboarding definition, it’s a key step that captures feedback and improves retention. In HR offboarding, this aligns with offboarding best practices, helping define what being offboarded means. It also adds clarity to employee offboarding meaning and reinforces what is offboarding in a strategic context.
8. How is knowledge transfer handled during offboarding?
During employee offboarding, knowledge transfer ensures continuity. It involves documentation, handovers, and mentoring. What is the role of HR in the offboarding process? HR facilitates these steps using structured tools. This helps define offboarding as more than just an exit—it’s a bridge between people and processes, further clarifying onboarding and offboarding meaning and what does offboarding mean long-term.



